08/30/2018 No views
As statistics show, the Russian forklift market is dominated by models with internal combustion engines, which are significantly larger than their counterparts that run on electricity. This equipment is operated in harsh conditions that require large resources. That is why one of the most important parameters to pay attention to is the fuel consumption of the forklift.
The cost of goods and work performed is directly calculated based on the fuel and lubricants used. The problem is that the fuel consumption of front loaders is much more difficult to determine than for a conventional vehicle, because for this equipment there is no defined standard for a range of 100 km.
Key Features
Fuel consumption, which in most cases is indicated by manufacturers, is as follows: number of grams / unit of power. That is why there is a rather strong discrepancy in the numbers, which creates even more confusion not only for the average person, but also for experienced drivers.
The fuel consumption indicated by the company that manufactures the equipment does not give any understanding of how much a particular engine will actually consume. It is not clear what the norm will be for an hour, a work shift or a whole month of operation. In this case, it is impossible to do without the use of certain theoretical knowledge and calculations.
What is the actual fuel consumption?
A clear and visual indicator is the amount of fuel in liters consumed per hour of equipment operation by operating enterprises and organizations. It should also be noted here that theoretical calculations of fuel consumption for a forklift will always be slightly higher than in practice, since in real conditions the load on the engine is less than in test conditions. Therefore, to determine fuel consumption for write-off, it is necessary to carry out control measurements.
A kind of timing was performed for the Komatsu 3-ton diesel truck of the BX50 series (FD30T-16), operating from 12 to 21 o'clock, i.e. 9 hours daily. Technological operations: unloading trucks, moving goods into cars. Fuel consumption readings for the engine on the FD30T-16 Komatsu 4D94LE loader were 2.5 l/h.
Thus, the fuel consumption indicators of a diesel forklift are influenced by such parameters as engine power and specific fuel consumption, and the duration of working hours when it operates at maximum speed. Cars with high mileage or, on the contrary, new ones, but not yet run-in, show higher fuel consumption than those on which the engine has been tuned. Fuel consumption higher than usual is shown by machines during special testing when operating at maximum load (for example, with an average rate of 3 l/h declared by the manufacturer, during a test a 1.5-ton loader can show a consumption of up to 5...6 l/h).
How to calculate fuel consumption rate
The fuel consumption rate for forklifts is determined by the following formula:
Q = (N*q)/(1000*R*k), where
N is an indicator of the power of specific diesel engines, which is installed in a specific model for which the calculation is being carried out.
q is the nominal fuel consumption, which is specified in the relevant documentation for the engine.
R is an indicator of the density of the diesel fuel used. This parameter is known initially, according to the approved standard (840 kg/m3 for winter and 860 kg/m3 for summer). For convenience, the general indicator is set at 0.85 kg/dm3.
k is a certain coefficient that reflects the time period in percentage terms when the front loader was operated in normal mode and the amount of time when it was used at maximum crankshaft speed.

Write-off of diesel fuel by engine hours
Standards are taken based on actual consumption. For the winter period, it is necessary to plan to increase fuel consumption by 12-15%. The rights of the tax authorities in the dispute that the enterprise has overestimated these standards (and for vehicles) is that these expenses may be prohibited from being classified as expenses.
Advice just in case: An inexperienced tax specialist may unknowingly claim that the write-off of fuel and lubricants can be carried out only on the basis of TRAVEL SHEET ESTABLISHED IN THE OKUD FORM THIS IS 3, 4-C, 4-P.
Then from his statement the question arises: SHOULD YOU ALSO WRITE A WAYWAY FOR A CHAINSAW, AND FOR A DIESEL GENERATOR, COMPRESSOR, ETC.??? Regulatory and methodological document RD R3112194-0366-03 (Download PDF format 0.1 Mb) In this The guiding normative and methodological document contains the values of basic fuel consumption standards for general purpose automotive rolling stock, fuel consumption standards for the operation of special vehicles, the procedure for applying standards and methods for calculating normalized fuel consumption during operation, reference standards for lubricant consumption, values of winter allowances, etc. .The guidance document is intended for motor transport enterprises, organizations, entrepreneurs, etc., regardless of the form of ownership, operating automotive equipment and special rolling stock on vehicle chassis on the territory of the Russian Federation. The proposed standards can be used as a basis for calculating departmental standards for the operation of special and technological vehicles.
Practical nuances
From the above information we see that almost all parameters when determining the fuel consumption of a forklift are known in advance, which cannot be said about the last coefficient (k).
To understand the situation, consider two examples:
- The equipment works at the railway station, loading and unloading railway cars. The shift is about 8 hours without a break. Workers are located on a platform that is located higher than the level of the special equipment, so the front loader forks do not rise to the height of the maximum boom reach. Maximum rotation of the engine crankshaft occurs only when the operator presses the pedal all the way, covering the distance between two certain points.
- The warehouse is open 24 hours a day. During the entire working day, there are two arrivals of trucks, which are unloaded in a few hours using the available equipment. It is at these moments that peak engine loads occur, but the rest of the time the crankshaft speed decreases, because the units perform warehouse work inside the warehouse without excessive intensity.
If we compare these two situations, then in the first case, the coefficient will be higher. This parameter takes into account peak loads - acceleration, downhill movement and lifting, during which the greatest use of equipment resources occurs. The calculation of fuel consumption for a front loader is determined based on the duration of its operation at peak crankshaft speeds from the total operating time (shift).
Fuel consumption standards for a front loader in practice
Using the SEM 650B front loader as an example, we will look at how the official fuel consumption data differs from the real picture. First, let's calculate the fuel rate using the above formula. The loader engine has a power of 220 hp. — a loader with a lifting capacity of 5 tons. The engine power of this loader is 162 kW, the time for which we will calculate fuel consumption is 1 hour, the specific fuel consumption for this machine is 220 g/kWh, any load percentage can be taken, and the fuel density, as mentioned above, is constant — 850g/l.
As a result, it turns out that for 100% load the fuel consumption will be 42 l/h, for 75% load - 31.5 l/h, and for 60 and 50% - 25.2 l/h and 21 l/h, respectively.
This forklift fuel consumption can be submitted to the organization's accounting department, and the figure obtained through such calculations will be considered an official indicator and will supplement the fuel consumption accounting data. However, in practice the situation is different.
In reality, you will need significantly less fuel. Of course, sometimes the technological process requires the engine to operate at the highest speeds, however, as a rule, this practically never occurs in real work. The specific fuel consumption figure, designated G in the formula, is almost impossible to verify. Equipment sellers often do not know what tests are carried out at factories to obtain this indicator - they simply obtain the value and report it to the buyer. Meanwhile, factories conduct tests closer to extreme conditions that are rarely encountered in real life, so the performance may differ significantly.
Thus, if you hear from a seller a questionable value for specific fuel consumption, be sure to ask what the value is in practice. Very often, large companies that sell special equipment specifically collect data from customers who are already working with their equipment in order to navigate real fuel consumption indicators. If you contact such a company, they will explain to you what fuel consumption is required for a specific front loader model in accordance with the expected operating conditions and load.
Do not miss:
Boats
What equipment manufacturers are doing to reduce fuel consumption
By the way, low fuel consumption is not an end in itself; it is important in combination with high productivity and machine dynamics, that is, when assessing how well and quickly the machine responds when performing work operations, how confidently it overcomes inclines, etc. What are manufacturers doing to increase the speed of technological operations while maintaining fuel consumption at the same level? For example, machines are equipped with a high-pressure hydraulic system, and this allows increasing the lifting speed. True, by increasing the speed of transmission of dynamic impact, it is necessary to ensure the tightness of the circuit (high-pressure hoses, hoses, etc.) through the use of high-quality materials. In order for forklifts of one of the economy-class brands to compete with more expensive machines in this indicator, the manufacturer will have to use a higher-quality transmission device. Accordingly, this will lead to an increase in the price of the car, and it will lose its main competitive advantage - affordability.
Another engineering technique is to separate the hydraulic flow to the steering and lifting equipment. The latest series of Komatsu BX50 forklifts (2...3 t capacity) uses a super-lift hydraulic system: twin pumps ensure that the steering and lifting mechanism operate independently of each other. The result is a stable rise at idle speed at maximum load, low fuel consumption.
The new Still Gmbh RX70 diesel loader is equipped with a hybrid drive and consumes 2.5 liters of fuel per hour (measurements were carried out on the basis of a 2.5 t model according to the new VDI 2198 criteria, i.e. after 60 operating cycles per hour). Hybrid drive technology involves the installation of a diesel or gas engine and an electric motor. This loader model uses a hydraulic pump that supplies oil to the hydraulic system as needed, rather than constantly, which also helps save fuel.
The creators of the Jungheinrich loaders of the DFG/TFG series 316-320 g/p 1.6...2 t, speaking about the advantages of the engine, emphasize that the large-volume industrial engine used (2.5-liter diesel engine with a power of 28 kW) already develops maximum speed at low speeds. torque, which also allows for low fuel consumption. For the Perkins 404C.22 engine model DFG 16 As, the manufacturer indicates a fuel consumption of 3.1 l/h according to the VDI cycle.
Thanks to the high-torque engine and hydrostatic transmission steering system, the Linde H16D diesel forklift (VVV/ADG engine) achieves a VDI fuel consumption of 2.3 l/h.
In the range of design developments of almost all leading forklift manufacturers there are models designed to operate on hydrogen fuel. It is clear that high-tech models cost 20...30% more than basic ones. And yet, serious attention is paid to this area as a unique intellectual contribution to the development of the brand.
New articles
- Kia repair at AutoMig Hyundai matrix chain or timing belt service center
- Viscous coupling and everything you need to know about it What is a viscous coupling
- Vortex Tingo car review - technical specifications and owner reviews Why Vortex Tingo is valued
- New SUV up to 600 thousand
- Tires and wheels for Nissan AD, wheel size for Nissan AD
- Tires and wheels for Skoda Fabia
- Ten most reliable cars over ten years old
- New comment What else did you like?
- Which Toyota RAV4 assembly is better: whose country of origin? What is the difference between Japanese and Russian assembled cars?
- Option to disable I-Stop (almost permanently)
Latest articles
- Test drive Skoda Octavia RS
- How much does a Lamborghini cost?
- What to do if the Volkswagen Polo Sedan does not start?
- Lifan X50: owner reviews with photos, characteristics, disadvantages
- Changing the oil in a robotic gearbox
- The process of changing the oil in the Focus 3 robot
- Is a complete replacement of antifreeze necessary? How many liters of antifreeze are needed for replacement?
- The engine does not pick up speed when you press the gas pedal: reasons
- What tire size is suitable for Lada Granta?
- The fuel pump does not pump gasoline
ooodrive.ru - The first in the world of motors. Engine structure. Transmission. Exhaust system. Tools and equipment
Fuel consumption rates per engine hour for diesel engines
Diesel fuel consumption standards for special equipment are on average 5.5 liters per 1 hour of operation in simple transport mode. When excavating soils in the first or second degree, the consumption is reduced to 4.2 liters per 1 hour of work.
If you additionally load or unload these soils, then for all MTZ-based excavators the consumption will be equal to 4.6 liters per 1 hour of operation.
Calculation of fuel consumption rates per hour, shift, month, etc.
O. Shevtsova
It is estimated that in the Russian market of counterbalanced forklifts the ratio of equipment with an internal combustion engine and an electric drive is 68%:32%. The predominance of forklifts is explained by the fact that industrialization processes (industrial and construction development) in our country are still a greater incentive for the loading equipment market than the development of warehouse logistics. That is, currently the main consumers of forklifts in Russia are enterprises and companies from various industries, and not logistics, although the latter is developing at a fairly rapid pace.
The operating features of the equipment also play a certain role: operation for a significant part of the year at low temperatures in open areas, coatings that are far from ideal, etc. A diesel engine requires lower costs for purchase, maintenance, and operation - it is a reliable, easy to maintain, powerful and efficient source of energy. In addition, such machines are produced in a wide range of carrying capacity (up to 43 tons) and with a wide range of attachments for performing various technological operations, and the exhaust gas purification system (particulate filters), used in the latest models of leading manufacturers, reduces harmful emissions by 70... 98%, which allows you to work indoors.
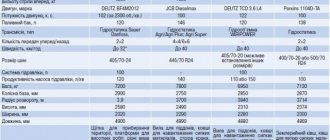
One of the characteristics of the “price of ownership” of a diesel forklift is fuel consumption. In the summary table of technical characteristics, the manufacturer often indicates specific fuel consumption in grams per unit of power measurement (hp or kW). Meanwhile, this parameter does not give an idea of how much a given engine will “eat” in practice, how much fuel will be consumed per hour, shift, per month, etc. For this, special techniques are used, one of which we will introduce readers.