Weight limits for vehicles on the road are set to reduce risks. Overloading of vehicles seriously threatens road safety and destroys the highways themselves. Each owner pays taxes, and at the same time wants to drive on high-quality and safe roads, and heavy-duty equipment that drives on them with a large overload breaks them. Therefore, the Ministry of Transport continues to fight against violators who exceed the established permissible weight standards for loaded vehicles by increasing fines.
Permissible truck weight
The weight of trucks is controlled by the State Traffic Inspectorate and is regulated by government decree No. 272. It specifies the permissible weight of a truck, maximum permissible axle load, permitted overload and rules for transporting goods that exceed these standards. Checking the weight of a truck is carried out according to two points:
- permissible weight;
- axle load.
Permissible weight - this parameter is set by the manufacturer and indicated in the car’s passport; it consists of the vehicle’s own weight and the cargo that it can transport. For example, if the PTS states that the maximum permissible weight of a vehicle is 20 tons, while its nominal weight is 10 tons, then it can transport cargo weighing no more than 10 tons. For certain types of freight transport, in addition to the Government decree, permissible weight standards are indicated freight transport:
If the weight of the road train together with its cargo exceeds 44 tons, then for its movement you need to issue a special permit, which will specify the time and route. If the truck weighs more than 80 tons, the traffic route is drawn up by traffic inspectors, who take into account the passage of the road train along certain sections of roads, taking into account bridges and overpasses. Axle load is the weight that is transferred by the wheels of a vehicle to the road surface. In this regard, the term “maximum axle load” was introduced, the meaning of which regulates the passage of vehicles on certain sections of roads and is indicated by special road signs.

The distribution of gravity along the axes of the car is not uniform. The front axle carries significantly less weight than the rear axle. Since the cabin is located in front of the car, and the main cargo is transported at the rear. The permissible loads on a vehicle axle are specified in the addendum to the Government Decree.
How to distribute the load on the axles?
Material address: https://bamap.org/information/smi/2017_12_29_94590/ Printing time: 09/03/2020 23:53:22 Source of information: https://business.truckandroad.ru/
The Russian government is introducing an automatic weight and dimensional control system for heavy vehicles on the country's roads. The operation of this system has so far caused complaints from road carriers. In an interview with the General Director, Taras Koval, a member of the Interindustry Expert Council (IEC), spoke about his vision of solving this problem and how foreign experience can help in this matter.
– Taras Ivanovich, at
the last meeting of the MOES you voiced your own vision of solving the issue of weight and dimensional control.
Please tell us about the origins of this concept... – The topic of compliance with weight and dimensional parameters is the main one for trailer manufacturers and body builders. The problems of Russian weight restrictions have been well known to me since the early 2000s - from the time I worked in international road transport. At international checkpoints, weighing was almost always carried out. And our cars did not always pass it successfully. Sometimes, even with a cargo weight of 20–21 tons, we found ourselves overloaded on the axles.
In 2013, Schwarzmüller headquarters received a request from Heineken. One of the world leaders in beer production was working to improve the efficiency of logistics in Eastern European countries and asked to make a proposal for semi-trailers that would have maximum load capacity, subject to Russian weight parameters and European packaging sizes.
But after consulting with our Austrian colleagues, we decided to try to calculate the special configuration of a three-axle curtain side semi-trailer for the Russian market and the geometry of a truck tractor in order to obtain maximum load capacity while complying with the requirements of Russian Government Decree No. 272.
– Why weren’t you satisfied with the equipment used by Austrian and German carriers?
– Firstly, we were talking about the UltraLight model with a dead weight of only 5200 kg. Secondly, when using such a semi-trailer with a 4x2 truck tractor, a wheelbase of 3600 mm and a total weight of the road train of 40,000 kg, the load on the drive axle of the tractor is 10,600 kg (overload according to our rules is 600 kg), and on the axle units of the semi-trailer - 22,600 kg ( overload of 100 kg is included in the measurement error; slide 1
). With these values, the payload of the road train is almost 27,300 kg and it fully complies with the weight and dimensional regulations of Austria, Germany and most EU countries.
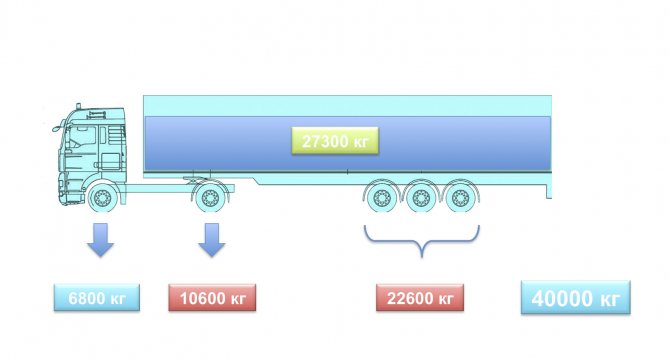
Slide 1
– Did you manage to create a package for Russia?
– Having gone through a lot of options for changing the location of axle units and the requirements for a truck tractor, the Austrian designers came to the conclusion: we will not be able to create a road train that, when loaded evenly, will not exceed the permitted axle limits and have a total weight of more than 39.5–39.6 tons. When using the European configuration and a truck tractor with a wheelbase of 3900 mm, it is possible to achieve a gross weight of 39.3 tons with a payload of almost 26 tons without exceeding axle loads. Transportation rates in Russia are relatively low, so the cost of manufacturing a modification of a semi-trailer specifically for Russia for the sake of 200–300 kg is not economically justified.
– In my opinion, 26 tons is a good indicator. Mostly they load 20–21 tons. Why does the issue of axial loads cause such a storm of emotions? Maybe you're not good at showing carriers possible design solutions?
– Many copies of the problem of weight restrictions have been broken. With varying degrees of success, a lot has been said about them in the last two years. But, apparently, only the introduction of automatic weight control with high penalties and the impossibility of reaching an agreement “on the spot” made the carrier community think seriously and look for a solution to the problem.
Since the very first meeting of the MOEC, held in January 2017, we have been discussing the weight problem every time. At the same time, we are introducing important, but generally minor changes to the “patchwork quilt” of Resolution No. 272. But problems in its implementation were and remain. Sometimes it seems to me that all these endless corrections are similar to the installation of components and assemblies from a modern car into the design of a car of the 1960s.
And the impetus for my current speech at the meeting was the previous discussion in a narrow group of MOES members about pressing problems with the implementation of automatic control systems. Olga Fedotkina was supposed to give a report on this topic. But after reading once again the large list of amendments, I could not resist and proposed my own concept based on European experience.
Taking this opportunity, I would like to thank Olga for agreeing to make a joint report and, as a starting point for presenting the material, based on the characteristics of the rolling stock used. This issue is closely intertwined with road safety and the safety of cargo during transportation, proposed by the famous surveyor Anatoly Shmelev.
The bulk of the freight rolling stock used today in Russia is certified according to European standards, which are very close to Russian ones. But at the same time, we have a problem with fines for violating axial restrictions, and in Europe it is minimal.
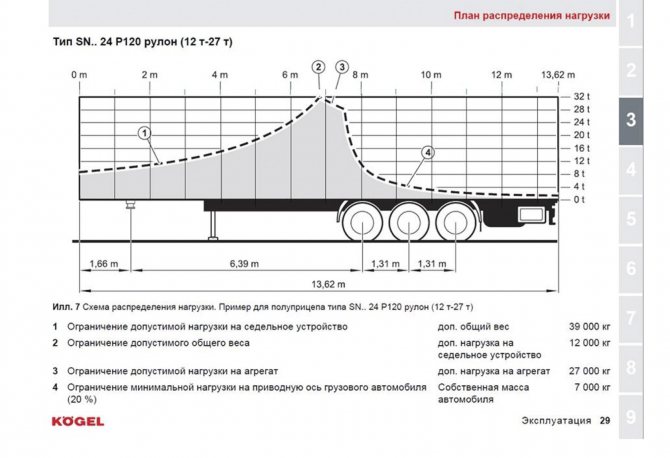
Slide 2
It's time to answer the second part of your question. Any unit of freight rolling stock has a diagram of the permissible technical load or a load distribution plan. If you look at this plan for a Kögel brand semi-trailer ( slide 2
), then we will see four main lines. This is a limitation of the permissible load on the fifth wheel (1), a limitation of the permissible total weight of the vehicle (2), a limitation of the load on axle units (3) and a limitation of the minimum load on the drive axle of the tractor to 20% (4).
This diagram is based on permissible technical loads. My proposal - to try to draw a diagram based on the loads allowed in Russia - for some reason caused fierce resistance from some members of the MOES. Apparently, they are satisfied with the current state of affairs...
– Your report also included a loading plan for single trucks...
- Really. On the presented plan ( slide 3
) for single trucks, the right side of the diagram shows the minimum load on the steering axle. When it is underloaded, there is a lack of friction force between the wheels and the road. In this case, steering the car into a turn without lateral steering becomes problematic.
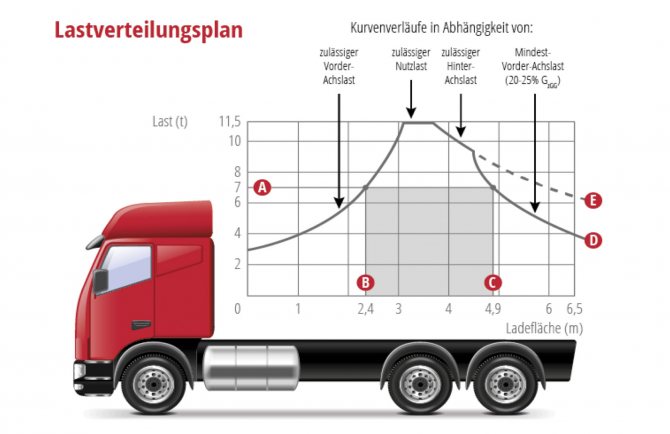
Slide 3
When loading dissimilar cargo, the center of gravity may shift ( slide 4
). If in the example given the center of gravity is located at a distance of 2.56 m from the front wall, then the load distribution plan allows for a payload of only 8 tons instead of the required 10 tons for transportation.
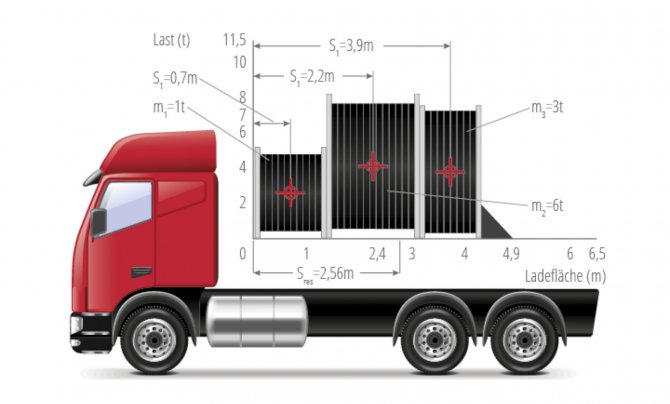
Slide 4
– But in such a situation, can the load be moved away from the front wall?
- You're right. However, this raises a number of problems. If it is necessary to place the load not close to the front wall, additional means of securing the load are required to prevent it from moving forward during sudden braking. Given our disgraceful level of understanding and implementation of the rules for securing cargo, packaging and, in general, preparing cargo for shipment, serious problems arise. Sometimes with fatal cases ( see photo below
).
Slide 5
And when legislative problems are added to the physical and technical problems - in the form of imposing unreasonable axial restrictions, then the situation with compliance with the necessary requirements becomes catastrophic. In order to avoid overload on the axles, it is necessary to underload the vehicle by more than 10% and arrange the load in various intricate combinations in an attempt to unload the drive axle of the tractor ( slide 5
). And yet the load still falls and the goods spoil!
– Your colleagues told you that there is software that can simplify the process of proper loading.
– Indeed, there is software that helps and allows you to efficiently arrange the cargo. For such a program to work correctly, it is necessary to weigh each piece of cargo and determine the center of gravity. Then, during loading, clearly arrange the pallets according to the drawn up plan.
But this takes a lot of additional time and human resources. The presence of these factors leads to an increase in the cost of logistics and the cost of goods. Given the restrictions in force in Russia, the weight of one pallet is on average lower than in Europe. This is also one of the increasing costs of logistics.
The option of installing checkweighers for each shipper is approximately the same in terms of efficiency. There is no answer to the question of who will pay the carrier for the additional working time spent on arriving at the scales, returning to the ramp in case of excess axial loads, and reloading. Many people don’t even understand that the loss of time of carriers is a real problem. When charging downtime for days, in the absence of control over the driver’s work and rest schedule, an additional hour or two of downtime is a work situation. And all these “exercises” are due to the existing illogical rules.
Slide 6
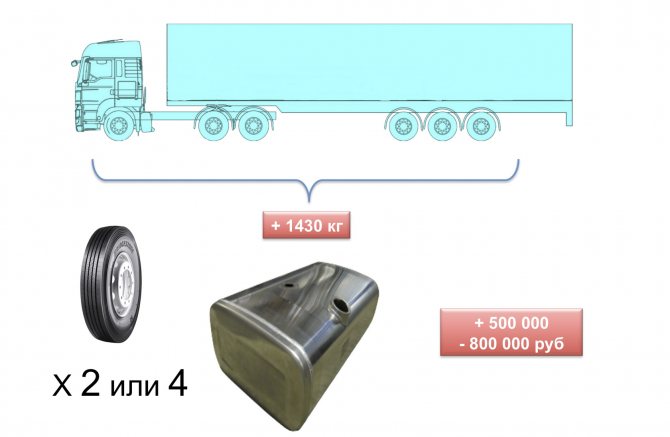
– If transportation of general cargo by a road train consisting of a two-axle truck tractor and a three-axle semi-trailer with a length of 13.6 m is associated with excess load on the drive axle, then why not use a three-axle tractor?
– This is exactly what the road workers propose to do ( slide 6
). A tractor with a 6x4 wheel arrangement is approximately 1400 kg heavier, has 4 more wheels, has higher fuel consumption, smaller fuel tanks, and a larger turning radius. The cost of such a tractor is higher, from 800 thousand rubles. In addition, the front part of the semi-trailer frame must have a longer section with a minimum side member height.
Slide 7
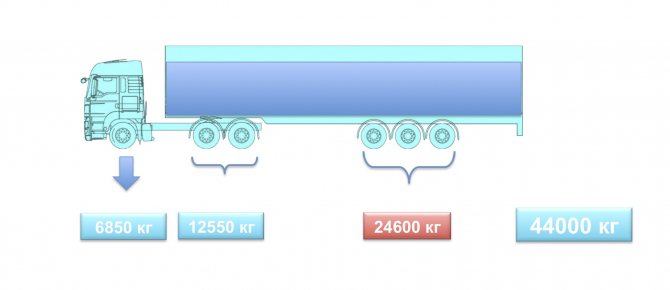
This requires its local strengthening and increased cost. The operating costs and initial cost of a 3+3 road train are higher, but the environmental friendliness is lower. And all because of axial restrictions. According to today’s rules, a “3+3” hitch can carry 44 tons ( slide 7
). But in this situation, with uniform loading, overload occurs on the axle units. There is a need to load unevenly, loading more of the front part.
– What is the situation in the transportation of bulk cargo?
– A tipper road train has a semi-trailer up to 10 m long, so it has a problem with overloading the axle unit ( slide 8
). The fifth wheel coupling can be moved forward, transferring the load from the axle unit of the semi-trailer to the steering axle of the tractor. This is exactly what they did for a famous road construction company. But the automatic weight control revealed an unexpected problem. The distance between the drive axle of the tractor and the first axle of the semi-trailer became less than 2.5 m. When passing the automatic weight control point, the system detected a group of four closely spaced axles. Instead of the permissible load of 10 tons on the drive axle, it gave seven, recording an “overload” of more than 30%. Resolution No. 272 does not directly indicate the distance between the axles of two vehicles. The legal battle between the carrier and Rostransnadzor continues.
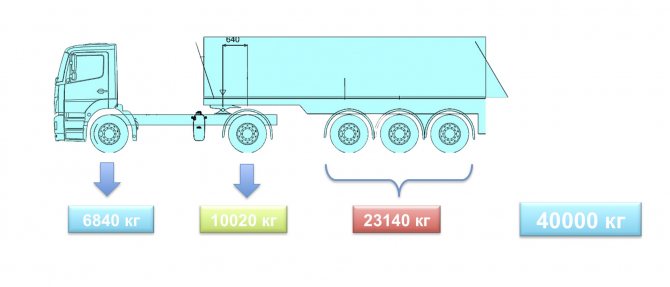
Slide 8
– In St. Petersburg, the story of controlling weight dimensions continues. When will it be possible to say that the overload has been overcome?
– Indeed, with the participation of NP Gruzavtotrans and regulatory authorities, an attempt is being made to bring carriers and shippers to work within the permissible dimensions. Before the start of control, the situation with overload was catastrophic ( slide 9
). The standards were exceeded by 30–80%! The picture from the dump truck website shows loads with a semi-trailer with a body volume of 28 m3.
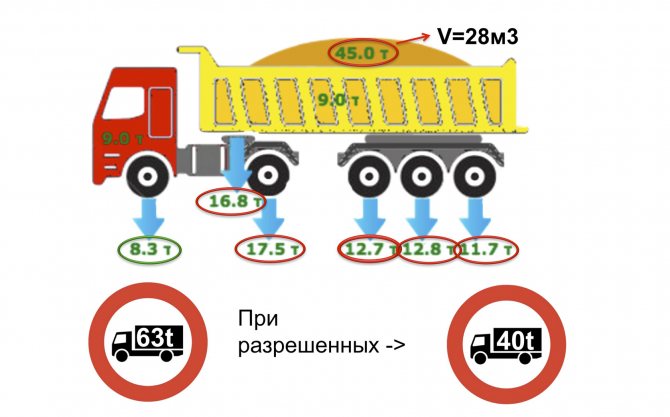
Slide 9
In practice, semi-trailers with bodies and 34m3 work. Their loads are even higher. If you configure a dump truck train for operation without overload as part of a 6x4 truck tractor and a three-axle semi-trailer, then the axle loads will look like this ( slide 10
).
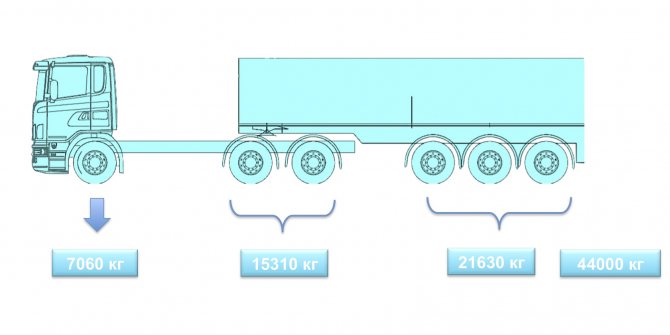
Slide 10
Now let’s compare these two road trains ( slide 11
). The operating costs and cost of a five-axle road train are noticeably lower compared to a six-axle one. Moreover, the latter can carry only one ton more. As soon as trailed manufacturers feel a steady demand for tipper semi-trailers in European configuration - with a body volume of up to 24 m3, then it will be possible to say that overload has been overcome. In the meantime, six-axle dump trucks contribute to overloading.
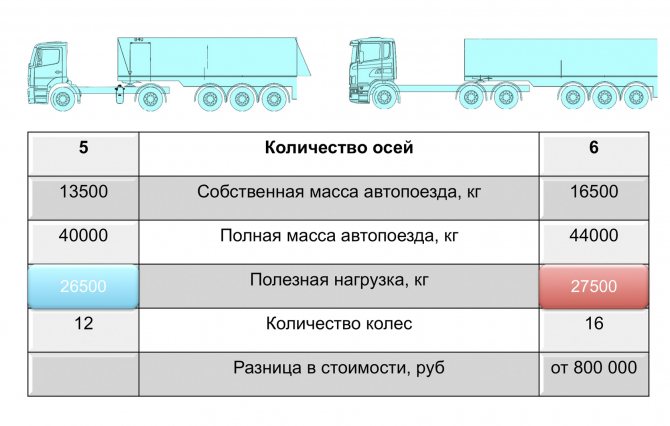
Slide 11
– How are things going with single dump trucks?
– On the weight distribution of a four-axle dump truck with an 8x4 wheel arrangement ( slide 12
) the absurdity of our restrictions is clearly visible. A load of 17 tons is allowed on a group of front steering axles with a single tire and an axle distance in this case of 1940 mm. In practice, it is difficult to load more than 13 tons. On rear dual drive axles with double tires and an axle distance of 1350 mm, only 16 tons are allowed. It is impossible to load to the full weight without violating the axle restrictions. Losses are more than 10%.
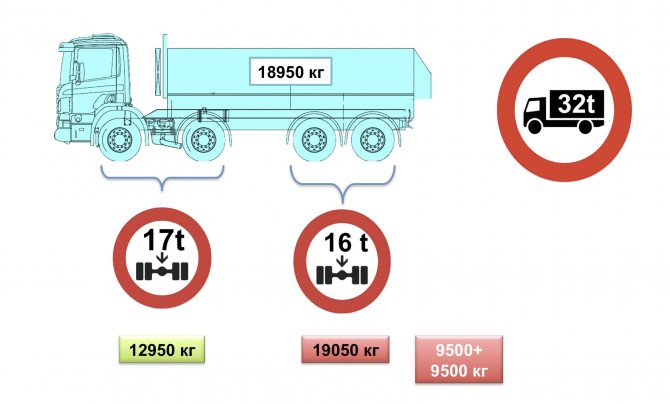
Slide 12
– In your report, you voiced the idea of a “careful approach” to the total weight of a road train of 44 tons. Please explain in more detail what this is connected with?
– There are two key points regarding the issue of increasing the gross weight of cars and road trains. Historically, in Russia, weight loads are a means of limiting the impact of a wheel on the road to reduce its destruction. In fact, weight restrictions are one of the main regulators of the country’s transport system.
The technological capabilities of modern trucks make it possible to transport significantly more than the standards established today. Some countries, for example, Finland, Sweden, Australia, significantly increase the permissible gross weight of multi-link road trains. And the Netherlands also has a permissible axial load. With a poorly developed railway network and problems with inland water transport, as well as in places with low population density, this approach is justified. In other cases, increased standards lead to a shift of cargo flow to motor transport. There were examples of the flow of cargo traffic when the total mass changed in the history of Germany. In my opinion, increasing the total weight of road trains in Russia to 44 tons is a mistake.
On the other hand, it is impossible to do without increasing the gross weight to 44 tons in a number of transportations that significantly affect the operation of other modes of transport and a number of industries. This is primarily container transportation and timber transportation. With the gross weight of the container being 32 tons and the tare weight of the road train being 12 tons, it remains within acceptable parameters.
The second nuance concerns the relationship between total weight and axle loads to ensure road safety and the possibility of manipulating axle loads.
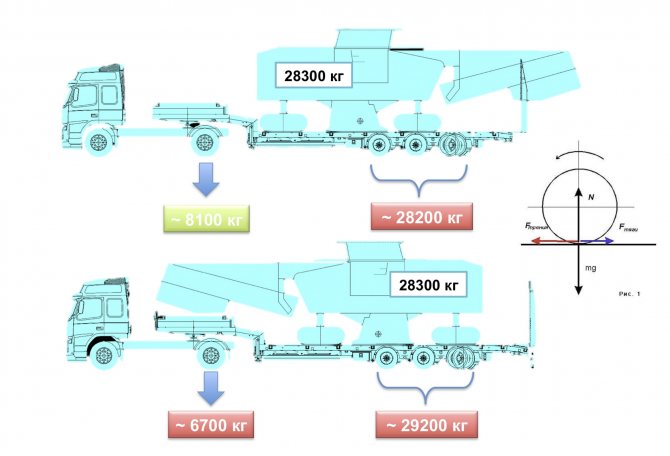
Slide 13
In the report I showed a slide ( slide 13
) transportation of a road milling machine weighing 28.3 tons on a trawl. It has a shifted center of gravity, so when placed on the trawl front or back, the axial loads change significantly. After the introduction in Russia of a permissible gross weight of 44 tons for six-axle road trains, we received a request from a carrier to create a road train consisting of a two-axle truck tractor and a four-axle semi-trailer-trawl. In the picture it is a three-axle one, but now we are talking about the minimum load on the drive axle of the tractor. To set the road train in motion, the load on the drive axle of the tractor must be sufficient so that the wheel does not skid. Maintaining a minimum load is important when driving on downhill turns to prevent “train folding”.
In Europe, the minimum load on the drive axle must not be less than 25% of the total weight. As can be seen from the picture, with any location of the road milling machine and the total weight of the road train of 44 tons, the load on the drive axle is below 25%. For Russia, with frequent difficult weather conditions, the requirement for a minimum load on the drive axle is especially relevant.
Maxim, this is not the first time we have communicated. Can I ask you a counter question?
–
An unexpected move...
– What technical solution would be the way out of this situation?
– Remembering the load diagram, the load needs to be moved forward, but...
– You have the right train of thought. If there is no way to move it forward, then use a sliding semi-trailer, moving the axle units back. In Russia they are not thinking about this yet.
– What manipulations can be done with 44 tons of gross weight on a six-axle road train?
– On the one hand, with 44 tons, there is a need to increase the load limit on a three-axle axle unit from the pan-European 24 to 27 tons. For us, this figure is still 22.5 tons. On the other hand, the “3+3” container ship combination, especially with the planned a significant increase in the recycling fee for tractors with a gross weight of more than 20 tons, more expensive than “2+4”, and heavier. To avoid overloading on a semi-trailer, container carriers began to use a semi-trailer with four spaced axles ( slide 14
). Even a person far from motor vehicles understands that with such an arrangement of axles, it is not only impossible to turn, but also difficult to drive. When passing the weight control, the first axle of the semi-trailer in the direction of travel is lowered and all axles correspond to the standard loads. In the transport position, the axle rises and the drive wheels of the tractor can bear a load of even more than 12 tons, and the three axle units of the semi-trailer - 26 tons. I don’t understand, who are we kidding by allowing the operation of this type of structure?
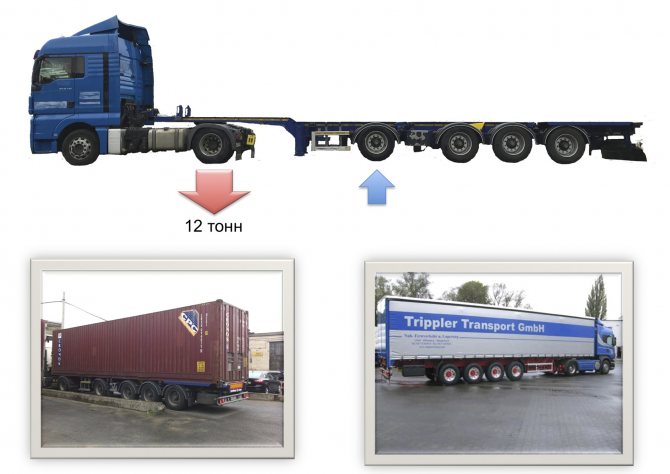

Slide 14
The story of problems due to current weight restrictions can be endless. Each type of transportation has its own.
– How do you see a way out of this situation?
– Prevention is easier than cure. Rules that are easy to follow are the solution to the problem. The system of weight and dimensional parameters must correspond to a simple formula for any design of a car and road train ( slide 15
): 7.5 t plus the sum of restrictions on all axles, except the steering one, should be 5–8% more than the total weight. Then it becomes possible to shift the center of gravity of the load without compromising road safety. The process of loading and securing cargo will be significantly simplified. Control will actually be based on the full mass. The vehicle's own weight is known and recorded in the vehicle's registration certificate, and the weight of the cargo is recorded in the consignment note. Their sum should not exceed the total mass. High fine for false declaration. It will become much more difficult to violate the axial parameters.
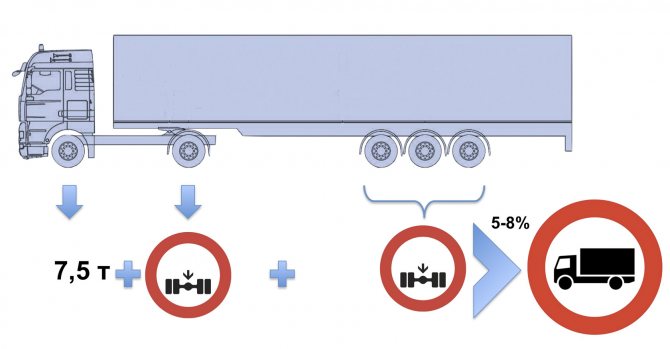
Slide 15
– What prevents the implementation of this idea?
– First of all, it is necessary to introduce a limit of 11.5 tons on the driving axle of a vehicle with dual-slope wheels and air suspension for all roads on which trucks are allowed.
– And here we come up against the categorization of roads...
- You are absolutely right. Before the introduction of the Plato system, one could only dream about this idea. The speech of Minister Maxim Sokolov citing the shocking, at first glance, difference in the impact on the road between a passenger car and a truck by 60 thousand times forced us to look for a source of information and suggested a solution to the problem.
In my opinion, the main problem lies in the incorrect fundamental approach of Soviet and now Russian road science. The very concept of “for roads designed for axial load” raises questions. How exactly is it calculated? How are oversized shipments taken into account? How is traffic intensity taken into account? On a country road with an asphalt thickness of 3 cm with a minimal road surface, if you can call it that, dump trucks with overload, which we talked about earlier, and the same cars with construction materials rarely drive through. The road has been in place for more than 10 years.
The Scandinavia and Sortavala highways near St. Petersburg are experiencing enormous overload from dump trucks and timber trucks. Seeing a caravan of dump trucks overloaded on Scandinavia, my German colleagues were shocked. “Is it that your roads are poorly built?! I can imagine the state of the German autobahns when caravans move along them with such overload.”
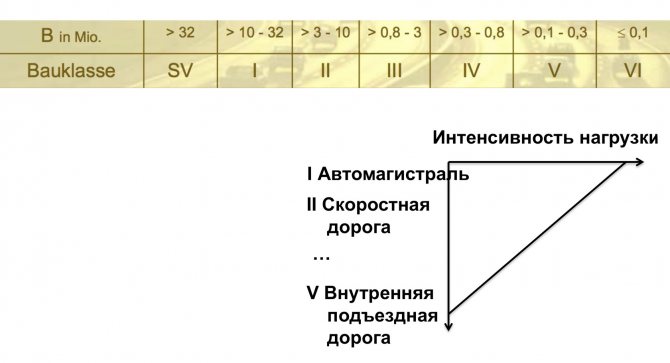
Slide 16
The main characteristic adopted in Germany and a number of other countries is much more logical and understandable. This is the intensity of the load. Roads are divided into construction classes ( slide 16
). The load intensity depends on the effect of the number of axles, the ratio of the 10-ton equivalent axle load to the actual axle load, the number of lanes, the lane width, the longitudinal topography of the road and the annual increase in traffic. And also on temporary factors: the durability of the road, the number of days of operation per year and the number of defrosts.
The load intensity indicator is measured by the equivalent of a 10-ton load. For the highest category of roads SV (autobahns and industrial roads) the equivalent is >32 million, and for class III (actually IV) only >0.8–3.0 million. Class III may already include regional roads. Each construction class of road has its own requirements for construction at a constant axle load, if truck traffic is allowed on this road.
In Germany and most other European countries, the maximum axle load is 10 tons. An exception of 11.5 tons is made only for the drive axle of a motor vehicle that has a dual-pitch tire and air suspension. The division of the axle load for driven axles depending on the installation of single or double slope wheels is an atavism in which the interests of road workers are higher than environmental problems and increased operating costs.
– How do you get the equivalent of a 10-ton load?
– This is exactly the same 60 thousand difference between the impact of a truck and a car on the road. The main difficulty in building and maintaining roads is taking into account the additional dynamic impact on road layers in the form of vibration. In terms of destructive ability, vibration can exceed the load from the wheel due to deformations in different directions.
Slide 17
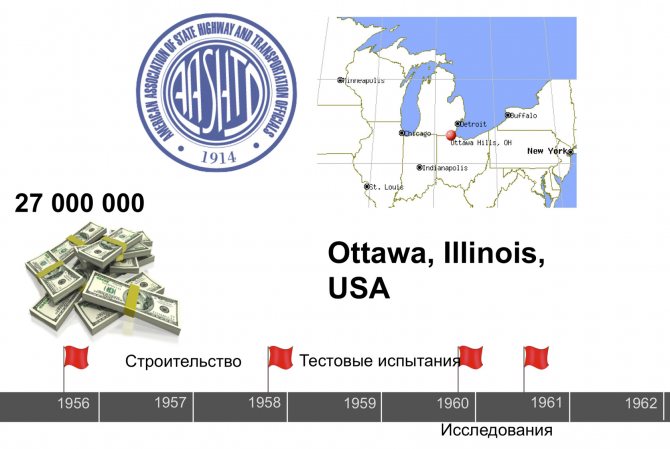
In the mid-twentieth century, near the American city of Ottawa (Illinois), one of the largest experiments in the world was conducted to study the impact of a car on a road structure ( slides 17–18
). The total cost of the experiment was $27 million. It was carried out from August 1956 to the summer of 1961. A two-lane, 7-mile long range with variable road depth was built.
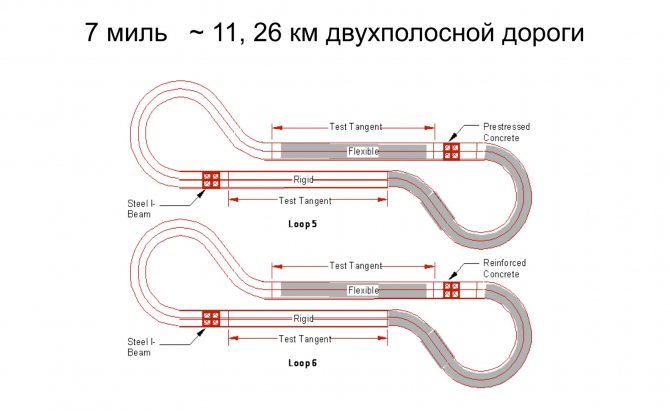
Slide 18
One of the main results of the experiment was the “Law of influence to the fourth power.”
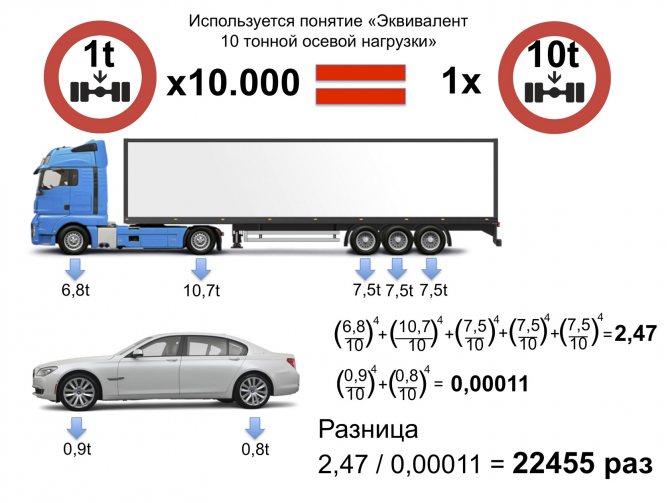
Slide 19
Today, in the German version, it reads as follows: 10 thousand axle loads of 1 ton affect the road in the same way as one of 10 tons. The slides show the difference between a classic five-axle semi-trailer and a BMW 5 Series ( slide 19
) and a trailed road train with a tandem trailer and a minicar (
slide 20
).

Slide 20
– What a big difference between the two comparisons...
- You're right. Therefore, in Germany, three states of a truck are considered: empty, partially loaded to a total weight of 30 tons, and loaded to a total weight of 40 tons ( slides 21-22
).
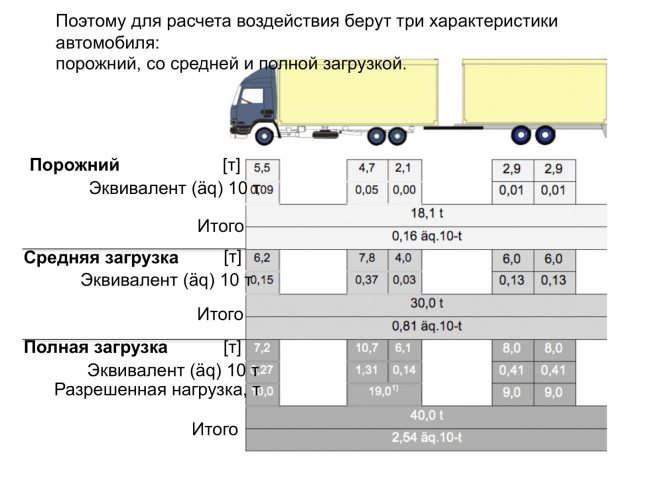
Slide 21
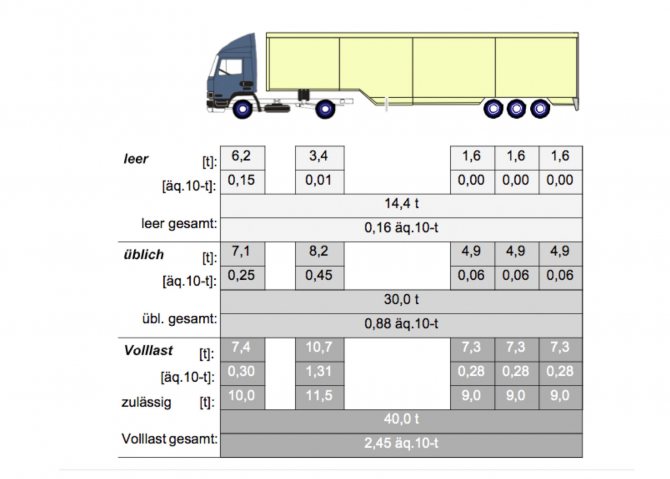
Slide 22
As a result of measuring traffic intensity and gross vehicle weight, a diagram of the share of trucks of different gross weights is obtained. An in-depth analysis of statistics allows you to calculate the efficiency of road construction and repair ( slide 23
). In Russia, unfortunately, even the total volume of the vehicle fleet is only approximately known.
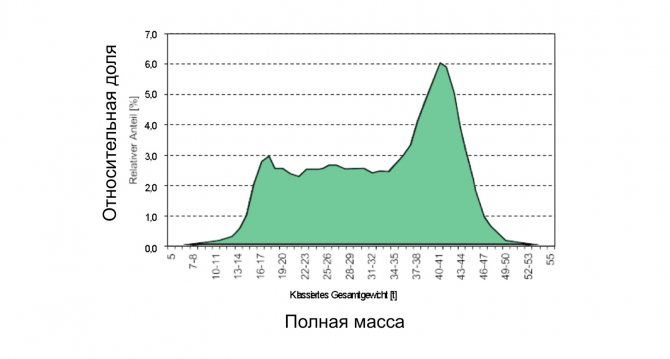
Slide 23
– Road workers say that the introduction of your proposal will potentially increase the load on the roads. Accordingly, additional funding will be required. Where can I get money?
– Firstly, road workers avoid direct dialogue. The principle of categorizing roads and the priority of road safety remains a “sacred cow” and is not discussed. My report and this interview are a desperate attempt to break the vicious “status quo”. Logistics problems on a national scale and the indignation of carriers are not yet of interest to road workers.
Secondly, a simple comparison of the indicators of the German Toll Collect system and the Russian “Platon” in terms of traffic intensity - and, indirectly, in terms of load intensity - raises questions for road workers to which one would like to receive answers. Before the tariff reduction for road tolls for trucks from a gross weight of 12 tons to 7.5 tons in Germany, about 2.4 billion km were paid monthly. In Russia - about 1 billion km. At the same time, in Germany the length of toll roads is 15.1 thousand km, and in Russia - 50.8 thousand km.
According to indirect indicators, fees from the operation of the Platon system should be 3.5–4.5 times more.
If we take these figures into account, then the intensity of the load on roads in Russia is on average 7–8 times lower and there should be no problems with the introduction of German weight parameters. Unfortunately, this statement is not entirely correct. According to indirect indicators, fees from the operation of the Platon system should be 3.5–4.5 times more. However, a difference of 2–3 times also leaves the possibility of introducing German weight restrictions.
The incentive for me to support the Plato system has always been the opportunity to cut the “Gordian knot” of axle load problems. But for now, the German Toll Collect will bring in more than 300 billion rubles annually, and the Russian Platon will bring in just under 37 billion rubles. in two years, the position of the road workers will be unshakable.
© 2020 BAMAP [email protected]
Design and programming: Abiatec
Fines for violating vehicle weight limits
The weight of the truck and the load on the axles are checked by a traffic police inspector. This happens at stationary posts specially equipped for this purpose, which, as a rule, are located at the entrance or exit from a populated area. Or transport is checked using mobile weighing units. The weighing method can be dynamic (while moving) or statistical (at a complete stop). Therefore, before starting to move a loaded vehicle, you should calculate the vehicle weight and axle load.

If the car is overloaded within 10%, the driver will pay a fine of 1.5 thousand rubles, an official - up to 15 thousand rubles, a legal entity - up to 150 thousand rubles. If the car is overloaded within 20%, the driver will have to pay 3-4 thousand rubles, an official 25-30 thousand rubles, and a legal entity or individual entrepreneur 300 thousand rubles.

If the overload of a vehicle reaches 50%, the amount of fines will increase: for the driver up to 10 thousand rubles, for officials 40 thousand rubles, for legal entities 400 thousand rubles. If, after weighing, the weight of the vehicle is more than 50%, then the driver will be issued a fine of up to 10 thousand rubles and will be deprived of his license for a period of 4 to 6 months. The official will pay 50 thousand rubles, and legal entities and private entrepreneurs will be fined 500 thousand rubles.
Who pays the fine for overloading a car?
0 6404 On the roads of Russia there are quite a lot of cars that are moving with obvious excess load, but visually this is noticeable only in passenger cars, which begin to sag, warp and...
— Read more —

Penalty for overloading passengers
0 5665 Drivers driving passenger cars should know what the fine is for excess passengers in 2020 and how to avoid the offense.
When transporting passengers in a personal car, great attention... — Read more —

Shipper's responsibility for overloading a truck
0 9033 When planning the transportation of large cargo, the driver must find out what responsibility the shipper is assigned for overloading a truck in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, and how can...
— Read more —

Permit for overloading a truck
0 14256 Drivers who regularly transport large items on a truck should know how to obtain a permit to overload a truck in 2020, what documents to submit and which state...
— Read more —

How much does it cost to overload baggage on a plane?
0 10669 When traveling, the most convenient transport remains air transport, which ensures the fastest arrival at your destination.
But even if you managed to get plane tickets at a low price, then at best with... — Read more —

Penalty for overload on axles
0 26704 Trucks are used to transport goods throughout the country, and there are standards that must never be exceeded.
If the vehicle load is too high, then this is not only a reason for... — Read more —