KamAZ-5320 is one of the first representatives in the line of trucks from the Kama plant. A massive onboard tractor is used to work with towed components GKB-8385. Its purpose is to carry out transportation processes in the construction industry and in almost all areas of industrial and economic activity.
The production of KamAZ-5320 started in 1968. For a long time, the Kama Automobile Plant did not dare to restyling the model. Minor cosmetic changes to the truck occurred only in 2000.
When considering the technical parameters of the vehicle, it becomes clear that the KamAZ-5320 is excellent for long- and short-distance transportation of goods. The tractor feels equally confident on city roads and on intercity highways. The car is adapted to Russian conditions and starts easily even in severe frosts.
The model was exported to 40 countries around the world, earning popularity not only in the domestic market, although it was originally created specifically for domestic consumers.
KamAZ-5320 is an onboard cargo tractor, which is often used as a road train for transporting various cargoes. The car is also known for the fact that many models for transporting medium-tonnage cargo were built on its basis.
Among them:
- base flatbed model 4325;
- truck 53212;
- truck tractor 5401;
- extended tractor 5325;
- dump truck 551.
Specifications
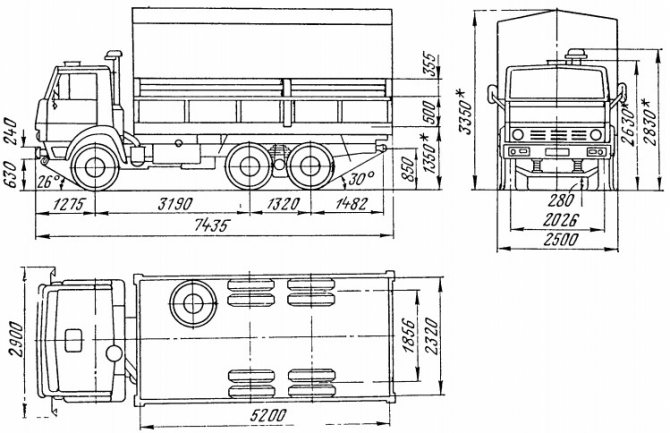
The overall dimensions of KamAZ-5320 (length - 7435 mm, height - 3350 mm, width - 2500 mm) allow you to transport quite massive loads. The tractor can be operated with a load of 8000 kg (45% on the front axle, 55% on the rear axle) and an additional trailer of 8000 kg. The wheelbase of the car is 3190 mm, and the minimum turning radius is 9300 mm.
The mass of the tractor itself is 7080 kg. The maximum load and trailer increase this figure to 26,500 kg. The vehicle's climbing angle is 30%.
The truck's run-out from 50 km/h is 700 m, and the braking distance at a speed of 60 km/h is 36.7 m. The maximum vehicle speed is 80 km/h.
Engine
The KamAZ-5320 engine is a 4-stroke diesel unit of the KamAZ-740.10 model with an 8-cylinder design. The engine has a V-shaped cylinder arrangement and closed-type nozzles. The power plant includes an all-mode speed controller, a dry air filter with a clogging indicator and a replaceable filter element, a fuel injection advance clutch and an electric flare device (EFD). Optionally, the unit is equipped with a pre-start heater PZD-30.
Motor characteristics:
- working volume – 10.85 l;
- rated power – 154 (210) kW (hp);
- maximum torque – 637 Nm;
- rotation speed – 2600 rpm.
- cylinder diameter – 120 mm.
Fuel consumption
Thanks to several upgrades, fuel consumption in the KamAZ-5320 was significantly reduced. This allowed the domestic model to compete on equal terms with foreign analogues. It was the economical processing of fuel that made the truck so popular in the domestic market. For 100 km of travel, the average fuel consumption is about 34 liters.
The tractor is equipped with two types of fuel tanks: 250 and 175 liters. This allows the car to cover significant distances without refueling.
Transmission
It represents the presence of a multi-stage system, which consists of a 2-stage divider and a 5-speed gearbox. This system makes it possible to obtain, in addition to standard gear regulators, auxiliary forward and reverse gears. Don't forget about installing the synchronizer.
The KamAZ 5320 gearbox has a 2-disc clutch, which does not lose its popularity. This device operates as a friction clutch, and can be activated using a hydraulic-pneumatic booster. It is controlled using peripheral springs.
The truck's run-out from a speed limit of 50 km/h is 700 meters, and the braking distance from a speed of 60 km/h is 36.7 meters. It is recommended to carry out maintenance of the KamAZ 5320 vehicle after every 100-kilometer run.
Maintenance service after 8,000 kilometers. Machine maintenance includes diagnostics of mechanical and electrical services, fastening work and lubrication of mechanical connections.
Suspension
The suspension located in front has springs (semi-elliptical, where there are sliding rear ends). The springs operate together with dual-type hydrotelescoping shock absorbers.
The rear-mounted suspension is a balancer type. There are also semi-elliptic leaf springs, sliding front and rear ends. Spring leaves have a T-shaped section.

Steering
Such a truck is controlled using a hydraulic booster, which is combined with a steering device.
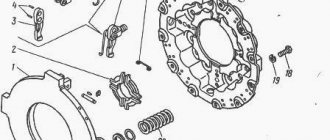
Brake system
In order to regulate the speed of the KamAZ-5320 and stop it effectively, a specialized device is used. Each of the 6 wheels of the truck has brake devices installed, which operate using a pneumatic drive mechanism. The dual-circuit device allows the driver to switch the rear axle into a capable position, while the trolley mounted at the rear starts separately.
Together with the brake of the parking sample, a spare brake was also combined, which is a motor retarder with a pneumatic drive. The trailer was equipped with a combined brake function. The brake system is presented in the form of drums. Steering is provided using a mechanism that consists of a screw with a nut and a rack-and-pinion piston.
Specifications
| Weight parameters and loads | |
| Vehicle curb weight, kg. | 6220 |
| Front axle load, kg. | 3210 |
| Car load capacity, kg. | 8860 |
| Total weight, kg. | 15305 |
| Front axle load, kg. | 4375 |
| Load on the rear trolley, kg. | 10930 |
| Engine | |
| Model | 740.11-240 |
| Type | diesel turbocharged |
| Rated power, gross, kW (hp) | 176 (240) |
| — at crankshaft rotation speed, rpm | 2200 |
| Maximum torque, Nm (kgcm) | 834 (85) |
| — at crankshaft rotation speed, rpm | 1200-1400 |
| Location and number of cylinders | V-shaped, 8 |
| Working volume, l. | 10,85 |
| Cylinder diameter and piston stroke, mm | 120/120 |
| Compression ratio | 16 |
| Supply system | |
| Fuel tank capacity, l. | 250 |
| Electrical equipment | |
| Voltage, V | 24 |
| Batteries, V/A hour | 2x12/190 |
| Generator, V/W | 28/1000 |
| Clutch | |
| Type | friction, dry, double-disc |
| Drive unit | hydraulic with pneumatic booster |
| Diameter of pads, mm. | 350 |
| Transmission | |
| Type | mechanical, ten-speed |
| Control | mechanical, remote |
| Transfer case | |
| Type | mechanical, 2-speed with lockable center differential |
| Control | pneumatic |
| Brakes | |
| Drive unit | pneumatic |
| Dimensions: | |
| Drum diameter, mm | 400 |
| Brake lining width, mm | 140 |
| Total area of brake linings, sq.cm | 6300 |
| Wheels and tires | |
| Wheel type | diskless |
| Tire type | pneumatic, chamber |
| Tire size | 9.00R20 (260R508) |
| Cabin | |
| Type | front, located above the engine, 3-seater |
| Execution | without a bed |
| Characteristics of a vehicle with a gross weight of 15305 kg | |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 90 |
| Maximum slope angle overcome by the vehicle at full weight, % | 30 |
| External overall turning radius of the vehicle, m | 9,3 |
| Optional equipment | |
| Engine preheater, seat belts, fog lights. | |
How many horsepower does Kamaz Master have?

Dakar 2011: how does KamAZ work?
About the KAMAZ -Master team sports trucks, it’s a little clear: what engine is installed? At what speed are they accelerating? Which parts were imported from other countries and which were imported from Russia? You asked? We are responsible!
In 1988, when Russian racers were just starting to talk about “ KAMAZ ” trucks, the equipment was practically serial: as the base part, the athletes chose the three-axle all-wheel drive KAMAZ-4310, which was reinforced with an engine producing up to 290 hp. (the serial “eight” produced 210 “horses”). ), a slightly modified cooling and lubrication system, a roll cage installed, stiffer springs, new springs and much more! In this version, KAMAZ-S4310 (“C.” Sport) made its debut at the European Elch Rally, and KamAZ took 2nd and 4th places in the individual competition and 1st place in the team competition.
Then a series of changes began: what kind of engines did racing trucks ! In 1989, the KAMAZ unit was increased to 400 horses. an experimental 10-cylinder engine (proved too unreliable), and in 1991 the specially developed G8 finally appeared with 430 hp. Of course, the powerful engine required significant changes to the transmission: the plant carried out an experimental gearbox and a new gearbox. Engineers also improved the suspension and power steering, and designed and installed a tire injection system.
Design of racing KAMAZ-4326-9
It should be noted that the first foreign component registered on a Russian sports truck was a British-made clutch, although KAMAZ used an increasing number of imported parts. For example, the next generation racing trucks (already two-axle!) received a 520-horsepower American Cummins engine. However, when Yaroslavl engines offered the YaMZ-7E846 power unit to the builders, KAMAZ chose the Russian turbodiesel: it offered high torque at low speeds and good performance on low-grade fuel.
With this engine, the mid-engine KAMAZ-49252 led KAMAZ participants to a triumphant podium at the Paris-Moscow-Beijing Marathon and allowed them to win the Golden Berber at Dakar'96. But then a new heart was introduced into the truck again: a 12-cylinder with more than a thousand horses! At Dakar98, such a KAMAZ failed because the transmission did not “digest” the enormous power. This prototype became the last Kama truck with a mid-engine: new marathon rules forced engineers to hastily create and test the new KamAZ-49256.
KAMAZ test at 970 hp!!! Take care of your spine.
Suprotek Racing Channel: TrucksTV in LCD:.
DT_LIVE. 920 hp Kamaz-Master and the Bakha Crimea railway roadstead
KAMAZ vehicles
on AUTO.ru:
After the 49256 model was created in a hurry, the unique KamAZ-4911 Extreme. a car that had no analogues in terms of driving performance, maneuverability and dynamics. Forty-nine-eleven was called a “flying truck”: this monster, from natural jumps, actually flew over the ground! In its debut in 2003, the high-speed heavy truck won the Russian Cup and Championship, Rally Desert Challenge, Khazar Steppes, Cappadocia and, most importantly, gold and bronze Dakar Berbers. Can you think of a better car? "It's possible!" answered the residents of Kamaz.
In 2007, the modern generation of sports trucks was born. KAMAZ-4326-9. This sports truck is equipped with a Russian YaMZ-7E846 engine with a volume of 18.47 liters. In the cabin, the V-shaped turbodiesel with 8 cylinders develops an impressive 830 hp. power and 3500 Nm of torque. However, the Yaroslavl turbo monster is not ideal: firstly, it is gluttonous (in a race the engine consumes more than 100 liters of diesel fuel per 100 kilometers), secondly, it is massive (1400 kg) and, thirdly, it has a modest resource. the engine operates until decommissioning approximately 30 thousand linear kilometers.
Turbodiesel engine YaMZ-7E846
The rest of the KAMAZ vehicles are equipped with mechanical refueling Master ” - a refrigerator of domestic and imported units: clutch. English SACHS, gearbox. German 16-speed ZF gearbox. Austrian Steyr, drive. Turkish Tirsan Kardan. If heavy KamAZ axles were installed earlier, now racing trucks received Finnish Sisu axles, but instead of standard disc brakes, domestic drum brakes were installed (brake from the Belgian company Wabco). Tires. Michelin 14.00 R20XZL tested.
KamAZ-4326 Vladimir Chagin
By the way, the car of seven-time Dakar winner Vladimir Chagin differs from other Blue Armada trucks: if a “regular” KAMAZ racing car costs about 200,000 euros, then a Chagin car with 900 horsepower costs 680,000 euros! What is the difference? Of everything created by the KAMAZ , this truck master is the simplest and fastest: the maximum speed is 180 km/h, and acceleration to 100 km/h takes less than 10 seconds. But visually Chagin differs only in small xenon headlights, as well as a cabin shifted forward.
What happens next? Most recently, KAMAZ engineers tested American Cummins engines, but there is no alternative to the Yaroslavl engine yet. The team’s engineers are also working on reducing the weight of trucks (currently vehicles weigh almost 9,200 kg, although for Dakar the weight can be 8,500 kg) and improving weight distribution (using Chagin’s prototype, we managed to achieve a “fifty-fifty” ratio). However, the improvement of modern cars. This is an attempt to make the best of the best: the KAMAZ sports car remains an uncompromising machine that allows you to win victories one after another.
Device
Each of the 6 wheels of KamAZ-5320 is equipped with brake devices that provide effective braking. The brake system itself operates from a pneumatic drive device having a 2-circuit design. It is capable of bringing the rear bogie and the front axle of the vehicle into working position independently of each other. The driver controls the drive via a foot lever mechanically connected to the brake valve.
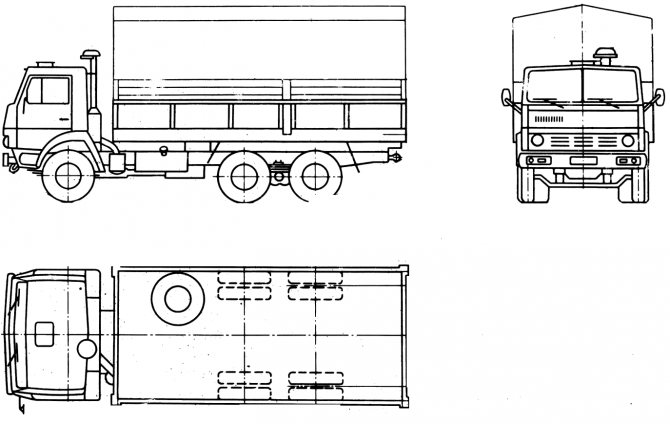
Appearance
So, what is the KamAZ-5320 if you look at it externally? This is a tractor that can work in conjunction with a GKB trailer. The carrying capacity is more than decent - 8 tons, but in a towed trailer you can grab another “eight”. The KamAZ 5320 body is a metal platform, where the side sides and the rear can be opened.
Thanks to this, it is possible to provide more comfortable loading and unloading of any cargo on each of the three sides. The floor was made using durable wood. If necessary, you can install a protective awning.
The very appearance of the car from the Kama plant is quite recognizable, because even today you can often see them on various roads. Although, it is worth admitting that the cabin, frankly speaking, is outdated and needs new modernization or, even better, a completely new design.
The curb weight of the 5320 model is just over 7 tons, the trailer weighs 3.5 tons. If the road train is fully loaded, its total weight can reach 26.5 tons. Now let's go over the dimensions.
The length of the KamAZ-5320 stretches 7.43 meters, and the width - 2.5 meters. The height of the truck is 3350 mm, but the wheelbase is 3190 plus 1320 mm.
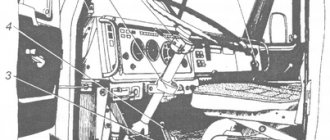
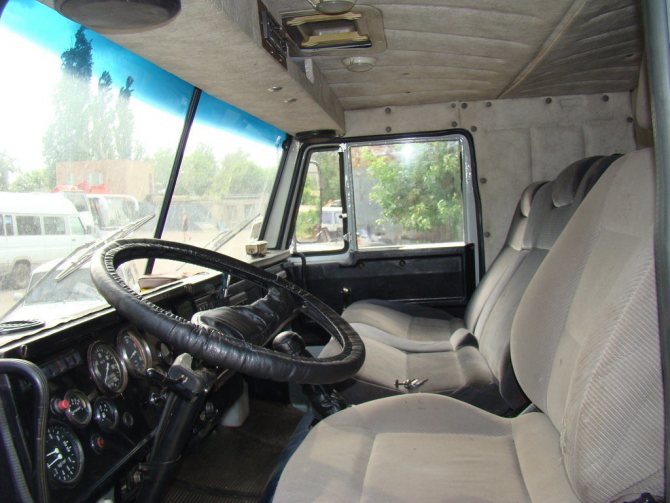
Cabin interior
The Soviet-made truck cabin was designed for three seats. At the same time, there was no separate space for “sleeping”. Despite this, the KamAZ interior has long been considered the standard of road comfort among trucks of that time.
What other truck could boast of excellent noise and thermal insulation, places for attaching seat belts, and a driver's seat that is adjustable to the weight of the driver. Moreover, the driver's seat was of the sprung type.
Of course, there are some drawbacks: the steering wheel is too large and the gearbox is somewhat inconveniently placed. However, you get used to everything, so you could always turn a blind eye to these shortcomings of KamAZ. The cabin interior has all the necessary instrumentation and indicators that allow the driver to read information about the condition of the car.
The dashboard has a signal system with excellent visibility of dials and switches. When compared with other similar trucks, the 5320 took a confident first place in ensuring the safety of the driver and the passengers sitting next to him.
The 5320 model is also different in that it has a two-pointer pressure gauge, a switch that adjusts the position of the platform, and an electronic speed sensor of the power unit.
But there are still a lot of shortcomings in the interior of the Kama car. The salon looks in a spartan style. The front (windshield) glass is divided into two parts. The pedals are not the most comfortable, which can make you tired on long trips. However, at the time when KamAZ trucks were just being produced, the interior was one of the best and most comfortable.

The KamAZ-5320 frame is a load-bearing spar type with riveted joints. It consists of two parallel beams-spars connected to each other by seven transverse beams.
Carbon steel is used as the material for manufacturing the structural components.
The front parts of the load-bearing side members have a beveled structure for mounting the suspension. Towing hooks are also attached to them. The front buffer is mounted to the supporting beams using bolts.
Use of KamAZ in army units
From the moment they entered production, KamAZ trucks also entered the formations of the USSR Armed Forces.
These vehicles received their baptism of fire at OKSVA during combat operations in Afghanistan, where they gained the reputation of being reliable and powerful vehicles, including when used in the highlands.
The main differences between the army modification of KamAZ and the civilian line were: reinforced design, a reshaped bumper, and the mandatory presence of a tire pressure regulation system. There were other differences, not so significant. The scope of use of machines in the army was quite wide:
- a vehicle for transporting bulk cargo and personnel;
- use as a platform for installing various radio equipment: command and control vehicles, launch control command posts and mobile stations for performing other tasks;
- armored vehicles for transporting personnel in the theater of military operations, this type of vehicle was not mass-produced, the armor was attached to the base model;
- vehicles for escorting convoys, gun trucks with ZU-23-3 weapons.
It’s worth talking about “gun trucks” in a little more detail; these vehicles initially had as their task the escort of convoys as they were escorted through the mountains of Afghanistan. A ZPU-4 or ZU-23-2 anti-aircraft gun was installed in the back of the vehicle.
These installations had the ability to fire all around, had an anti-aircraft elevation angle and powerful cartridges; their shells and bullets could reach the enemy at long range and altitude. This made it possible to effectively combat ambushes on the road.
The armoring of such vehicles was often makeshift and consisted of hanging the cabin doors with bulletproof vests, less often they were sheathed with metal.
The charger installation itself was covered with doors from the infantry fighting vehicle or other improvised means, the purpose of which was to protect the installation crew, although it was minimal. Subsequently, the production of such support products was suspended.
The armored Urals and KamAZs, which appeared during the Caucasian Wars and were nicknamed “Pokemons,” are also a product of handicraft production; there are practically no such vehicles in the series. Although their high efficiency in operation has been proven.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Model | KamAZ-5320 | KamAZ-53212 |
| Load capacity, kg | 8000 | 10000 |
| Curb weight, kg | 7080 | 8000 |
| Including: | ||
| to the front axle | 3320 | 3525 |
| on the trolley | 3760 | 4475 |
| Total weight, kg | 15305 | 18225 |
| Including: | ||
| to the front axle | 4375 | 4290 |
| on the trolley | 10930 | 13935 |
| Permissible trailer weight, kg | 11500 | 14000 |
| Gross weight of the road train, kg | 26805 | 32225 |
| Max vehicle speed, km/h | 80 | 80 |
| The same, road trains | 80 | 80 |
| Vehicle acceleration time to 60 km/h, sec. | 35 | 40 |
| The same, road trains | 70 | 90 |
| Max. climbability by car, % | 30 | 30 |
| The same, by road train | 18 | 18 |
| Vehicle run-out from 50 km/h, m | 700 | 800 |
| Car braking distance from 60 km/h, m | 36,7 | 36,7 |
| The same, road trains | 38,5 | 38,5 |
| Control fuel consumption, l/100 km of vehicle: | ||
| at 60 km/h | 23,0 | 24,4 |
| at 80 km/h | 29,6 | 31,5 |
| The same, road trains: | ||
| at 60 km/h | 32,5 | 33,0 |
| at 80 km/h | 43,7 | 44,8 |
| Turning radius, m: | ||
| on the outer wheel | 8,5 | 9,0 |
| overall | 9,3 | 9,8 |
TO
category:
Kamaz Ural cars
P
publication:
Lubrication system for KamAZ-5320, KamAZ-4310 and Ural-4320 engines
H
read more:
Design and operation of the KamAZ-5320, KamAZ-4310 and Ural-4320 engine lubrication system
Lubrication system for KamAZ-5320, KamAZ-4310 and Ural-4320 engines
The lubrication system is designed to accommodate, clean and cool the oil, supply purified and cooled oil to the rubbing parts of the engine in order to reduce their friction, wear and heating and remove the resulting wear products.
Based on the principle of supplying oil to rubbing surfaces, the lubrication system is combined: some of the rubbing parts are lubricated under pressure, some by splashing, and some by gravity. Oil under pressure is supplied to the most loaded rubbing parts: main and connecting rod bearings of the crankshaft, camshaft bearings, rocker arm bushings, fan drive fluid coupling, high-pressure fuel pump and compressor. A pulsating oil supply is provided to the upper spherical supports of the pusher rods. The remaining rubbing surfaces of the parts are lubricated by oil splashed and flowing from various surfaces. The bulk of the oil is located in the engine sump (“wet sump”).
Oil circulation in the system is carried out by an oil pump at a nominal pressure of 400...550 kPa (4.0...5.5 kgf/cm2) and its permissible reduction to 150 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) at low crankshaft speeds. Oil purification is initially carried out in the oil receiver mesh filter, then in a full-flow fine filter and in a parallel-connected centrifugal filter for additional oil purification. The oil is cooled in the radiator by an air flow created by the cooling system fan. Crankcase ventilation (removal of exhaust gases and fuel vapors that penetrate the engine crankcase and deteriorate the quality of the oil) is carried out through a labyrinth-type breather.
Promotional offers based on your interests:
The condition of the lubrication system is monitored using a pressure indicator and a lamp indicating an emergency drop in oil pressure. A lamp is provided to indicate that the fine oil filter is clogged.
The lubrication system uses: in summer, at temperatures above plus 5 °C, M-10G2K oil, in winter, at temperatures below plus 5 °C, M-8G2K oil. Substitute (all-season) - DV-ASZp-10V oil.
The filling capacity of the engine lubrication system of the KamAE-5320 vehicle is 26 liters, the KamAZ-4310 vehicle is 24.5 liters, and the Ural-4320 vehicle is 23.7 liters.
Promotional offers:
Read more: Design and operation of the KamAZ-5320, KamAZ-4310 and Ural-4320 engine lubrication system
TO
category: — Kamaz Ural cars
Home → Directory → Articles → Forum
History of creation [edit | edit code]
The prototype of the future KamAZ-5320 was developed at ZIL and was called ZIL-170. The first ZIL-170 was built in 1968. It had an engine from the Yaroslavl Motor Plant (YaMZ). Already in May 1969, the first prototype of the ZIL-170 vehicle passed its first tests on the Uglich-Rybinsk section. But after the adoption of the resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR “on the construction of a complex of factories for the production of heavy-duty vehicles in Naberezhnye Chelny,” it was decided to transfer further development and subsequent assembly of the ZIL-170 to KamAZ. At the same time, the name of the car was changed to KamAZ-5320. The first experimental KamAZ-5320 rolled off the assembly line in 1974.
The first serial KamAZ trucks rolled off the assembly line on February 16, 1976. According to the tradition of those years, the trucks from the first batch were decorated with the slogan “Our gift to the XXV Congress of the CPSU.”
Design of the KamAZ-5320 car [edit | edit code]
The general layout of the KamAZ-5320 is typical for trucks of that time. The three-seater cabin of the car is located above the engine and, using a torsion mechanism, tilts forward, opening access to the engine. The engine, clutch and gearbox form a single power unit mounted on front, rear and support mounts.
Power units and transmission [edit | edit code]
The KamAZ-5320 was equipped with four-stroke V-shaped eight-cylinder diesel engines KamAZ-740 10.85 liters with a power of 210 hp. s., at a maximum speed of 2600 per minute. A fire on April 14, 1993 destroyed the KamAZ Engine Plant, and production of KamAZ-740 engines was temporarily stopped. In this regard, until the plant was restored in December 1993, diesel engines of the Yaroslavl Motor Plant YaMZ-238 with a power of 240 hp were installed on KamAZ family vehicles. KamAZ-740 diesel engines used design solutions that were new to the domestic automotive industry at that time or had not yet found widespread use, for example, a nitrided crankshaft or a full-flow oil filtration system with a centrifuge. Automatic monitoring of the correct operation of the cooling system is carried out by a fluid coupling in the fan drive and two thermostats. The cooling system is closed and designed for constant use of Tosol coolant. An air purification system has been introduced with a dry type filter and automatic dust extraction from the filter using an ejector operating using the energy of exhaust gases. Other innovations include colloidal-graphite coating of the piston skirts, removable metal-ceramic valve guides, molybdenum coating of the lower piston ring, and an active-reactive exhaust silencer. The KamAZ-5320 power units use double-disc clutches. The hydraulic drive of the clutch control mechanism has a pneumatic amplifier, making it easier to use the pedal. A special feature of the KamAZ tractor transmission is a divider (multiplier) - an additional two-stage gearbox installed after the clutch in front of the main gearbox. One gear of the divider is made direct, and the second is overdrive. The gearbox itself is a five-speed one, synchronized in second, third, fourth and fifth gears. The box control is remote, with a mechanical drive. In the divider, the gears are switched by a pneumatic drive. The cardan transmission is an open type and consists of two tubular shafts. Cardan joints on needle bearings with a constant supply of lubricant. The main gear of the drive axles is made double: a pair of bevel gears with spiral teeth and a pair of cylindrical helical gears. The middle axle has a lockable symmetrical center differential.
Suspension [edit | edit code]
The front suspension springs (semi-elliptical, with sliding rear ends) work in conjunction with double-acting hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers. The rear suspension is of the balancing type. Its springs are also semi-elliptical, with sliding front and rear ends. The leaf springs have a T-shaped section.
Wheels and tires [edit | edit code]
The car was equipped with discless wheels with removable side and lock rings. Tires are radial type, 12-ply, sizes 260-508R (9.00-20), usually with a universal tread pattern.
Brakes [edit | edit code]
KamAZ-5320 is equipped with several brake systems: service, parking, auxiliary and spare. The brakes on all wheels are drum type, with two pads. The service brake drive is pneumatic, dual-circuit, with separate action for the wheels of the front axle and the wheels of the rear bogie. When parked, the car is held by the brake mechanisms of the wheels of the rear trolley, which in this case are driven by spring energy accumulators. The auxiliary brake mechanisms are installed in the exhaust pipes of the muffler. Their action is based on creating back pressure in the gas exhaust system through dampers that block the flow sections. In the event of an emergency failure of one of the main systems, the car can be stopped with a spare parking brake. The driver controls the service brakes by pressing a pedal connected by levers and rods to a two-section brake valve. To the right of the driver's seat there is a valve with a parking brake handle. The spare system is activated together with the parking system, and the auxiliary system is activated using a push-button switch located on the cabin floor under the steering column.
Steering [ edit | edit code]
The steering includes a hydraulic booster combined with a steering mechanism.
Tow hitch [ edit | edit code]
At the rear of the frame there is a towing device with two-way shock absorption. It is designed for continuous operation with a trailer with a total weight of up to 11.5 tons.
KAMAZ 5320 – Wikipedia
| Brand: | KamAZ-740.10 |
| Type: | diesel |
| Volume: | 10,850 cm3 |
| Maximum power: | 210 l. s., at 2600 rpm |
| Maximum torque: | 637 Nm, at 1500 rpm |
| Configuration: | V8 |
| Cylinders: | 8 |
| Valves: | 16 |
| Cylinder diameter: | 120 mm |
| Piston stroke: | 120 mm |
| Compression ratio: | 17 |
| Supply system: | diesel |
| Cylinder operating order: | 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8 |
| Recommended fuel: | d/t |
manual 10-speed
| Manufacturer: | KamAZ |
| Type: | mechanical |
| Number of steps: | 10 |
| Gear ratios: | |
| 1st gear: | 7,82 |
| 2nd gear: | 6,38 |
| 3rd gear: | 4,03 |
| 4th gear: | 3,29 |
| 5th gear: | 2,50 |
| 6th gear: | 2,04 |
| 7th gear: | 1,53 |
| 8th gear: | 1,25 |
| 9th gear: | 1,00 |
| Reverse gear: | 7.38 and 6.02 |
| Switching: | floor lever |
The main gear of the drive axles is double, the gear ratio is 6.53. Can also be 5.43; 5.94; 7.22
| Height: | 2630 (without awning) |
| Max. speed: | 90 km/h. |
Predecessor
| Load capacity: | 10,000-20,000 kg |
| Fuel consumption: | 34 l |
| Volume of the tank: | 210 l |
| Designer: | Lev Samokhin, Alexander Setranov, Vsevolod Vyazmin, Georgy Fest |
KamAZ-5320 is a Soviet and Russian three-axle flatbed truck-tractor with a 6 × 4 wheel arrangement, produced by the Kama Automobile Plant (KAMAZ) from 1976 to 2001. It became the first car model under the KamAZ brand. Intended incl. and for permanent work as a road train with a trailer. The body is a metal platform with opening side and rear sides and an awning. The cabin is three-seater, all-metal, tilting forward, equipped with seat belt attachment points. The main trailer is of the same size.
History of creation[ | ]
The prototype of the future KamAZ-5320 was developed at ZIL and was called ZIL-170. The first ZIL-170 was built in 1968. It had an engine from the Yaroslavl Motor Plant (YaMZ). Already in May 1969, the first prototype of the ZIL-170 vehicle passed its first tests on the Uglich-Rybinsk section. But after the adoption of the resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR “on the construction of a complex of factories for the production of heavy-duty vehicles in Naberezhnye Chelny,” it was decided to transfer further development and subsequent assembly of the ZIL-170 to KamAZ. At the same time, the name of the car was changed to KamAZ-5320. The first experimental KamAZ-5320 rolled off the assembly line in 1974.
The first serial KamAZ trucks rolled off the assembly line on February 16, 1976. According to the tradition of those years, the trucks from the first batch were decorated with the slogan “Our gift to the XXV Congress of the CPSU.”
Based on the KamAZ-5320, the family created the KamAZ-5410 truck tractor, KamAZ-5511 dump truck, KamAZ-53212 extended flatbed truck, chassis, as well as a family of two-axle analogues (extended KamAZ-5325 and basic KamAZ-4325 flatbed, KamAZ-43255 dump truck , tractor unit). Production of the first two models of the 5320 family began in 1977, the rest - later. All models of this family had a similar design and were largely unified.
Design of the KamAZ-5320[ | ]
The general layout of the KamAZ-5320 is typical for trucks of that time. The three-seater cabin of the car is located above the engine and, using a torsion mechanism, tilts forward, opening access to the engine. The engine, clutch and gearbox form a single power unit mounted on front, rear and support mounts.
Power units and transmission[ | ]
The KamAZ-5320 was equipped with four-stroke V-shaped eight-cylinder diesel engines developed by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant of 10.85 liters, with a power of 210 or 180 hp. s., at a maximum speed of 2600 per minute. The diesel engines for the first KamAZ trucks used design solutions that were new to the domestic automotive industry at that time or had not yet found widespread use, for example, a nitrided crankshaft or a full-flow oil filtration system with a centrifuge. Automatic monitoring of the correct operation of the cooling system is carried out by a fluid coupling in the fan drive and two thermostats. The cooling system is made closed and was designed for the constant use of Tosol coolant. An air purification system was introduced with a dry-type filter and automatic dust extraction from the filter using an ejector powered by the energy of the exhaust gases. Other innovations include colloidal-graphite coating of the piston skirts, removable metal-ceramic valve guides, molybdenum coating of the lower piston ring, and an active-reactive exhaust silencer. The KamAZ-5320 power units use double-disc clutches. The hydraulic drive of the clutch control mechanism has a pneumatic booster, making it easier to use the pedal. A special feature of the KamAZ tractor transmission is a divider, or multiplier - an additional two-stage gearbox installed after the clutch in front of the main gearbox. One gear of the divider is made direct, and the second is overdrive. The gearbox itself is a five-speed one, synchronized in second, third, fourth and fifth gears. The box control is remote, with a mechanical drive. In the divider, the gears are switched by a pneumatic drive. The cardan transmission is an open type and consists of two tubular shafts. Cardan joints on needle bearings with a constant supply of lubricant. The main gear of the drive axles was made double: a pair of bevel gears with spiral teeth and a pair of cylindrical helical gears. The middle axle has a lockable symmetrical center differential.
Specifications [ edit | edit code]
- Wheel formula - 6 × 4
- dimensions
- Length, m - 8.395
- Width, m - 2,500
- Height, m - 2,830
- Rear trolley base, m - 1,320
- Front wheel track, m — 2.010
- Rear wheel track, m — 1,850
- Lowest ground clearance, cm - 34.5
- Loading height, m - 1,370
- Weight parameters and loads, vehicles
- Vehicle curb weight, kg — 7500
- Car load capacity, kg - 8000
- Maximum weight of towed trailer, kg - 8000
- Gross weight, kg - 15,305
- Engine
- Model - KamAZ-740.10
- Type - diesel naturally aspirated
- Power, l. With. — 210 or 180
- Location and number of cylinders - V-shaped, 8
- Working volume, l - 10.85
- Lubrication system volume, l – 28
- Transmission
- Type - five-speed mechanical with two-stage divider (5*2)
- Clutch - dry double disc
- Cabin
- Type - located above the engine.
- Execution - without bed
- Wheels and tires
- Wheel type: discless
- Tire type - pneumatic, tube
- Tire size - 9.00R20 (260R508)
- Tread patterns - Diamond and Houndstooth.
- Platform
- Side platform, with metal folding sides
- Internal dimensions, mm - 5200x2320
- General characteristics
- Maximum speed, km/h - 85
- Average fuel consumption for a road train, l/100 km - 35
- Fuel capacity, l - 170
- The angle has been overcome. rise, no more, % - 30
- External overall turning radius, m - 9.3
- Braking distance for a road train with a full load from a speed of 40 km/h, m - 21
Design of KamAZ-5320 flatbed truck
Frame, suspension and wheels
The truck received a ladder-type spar frame, which is equipped with reinforcements. A towing device with double-sided shock absorption was attached to the rear of the frame, which is designed for constant work with a trailer with a total weight of 11.5 tons. The frame has a buffer at the front.
The continuous front axle of the KamAZ-5320 was connected to the frame using semi-elliptical springs with sliding ends and double-acting telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, and the rear axles - a spring-balance suspension. The leaf springs have a T-shaped section.
Discless wheels with removable side and lock rings were attached to the front axle and rear axles. Tires are radial type, size 260-508R, 12-ply, with a unique tread pattern. The front wheels were fastened to the spokes of the hubs with five clamps, studs and nuts. The rear twin wheels were mounted using the rim of the rear inner wheel on the conical surface of the spokes of the rear hub.
Brake system
The KamAZ-5320 flatbed truck received several brake systems: service, auxiliary and spare. The brakes on all wheels are drum type with two shoes. The service brake drive is pneumatic, dual-circuit, with separate action for the wheels of the front axle and the wheels of the rear bogie.
In the parking lot, the truck was held by the brake mechanisms of the wheels of the rear bogie, which in this case were driven by spring energy accumulators installed on the bridge.
The KamAZ-5320 auxiliary brake mechanisms are installed in the exhaust pipes of the muffler. Their action is based on creating back pressure in the gas exhaust system using dampers that blocked the flow sections. In the event of an emergency failure of one of the systems, the truck can be stopped with a spare parking brake.
The driver controlled the service brakes from the cab using a floor pedal, which is connected by levers and rods to a two-section brake valve. In the cockpit, to the right of the driver's seat, there was a valve with a parking brake handle. The spare brake system was activated along with the parking one, and the auxiliary one was activated using a push-button switch, which was located on the cabin floor under the steering column.
Engine, clutch and gearbox
The engine, clutch and gearbox of the KamAZ-5320 truck were a single power unit, which was installed on the frame on the front, rear and supporting supports.
As a power unit, the KamAZ-5320 truck received a four-stroke V-shaped eight-cylinder diesel engine KamAZ-740 with a displacement of 10.85 liters and a power of 210 or 180 hp.
at 2600 rpm. The engines were distinguished by design solutions that were progressive
for the domestic automotive industry at that time:
- nitrided crankshaft;
- a full-flow oil filtration system with a centrifuge, which increased engine life;
- automatic control of the correct operation of the cooling system using a fluid coupling in the fan drive and two thermostats;
- the closed cooling system of the KamAZ-5320 truck is designed for the constant use of Tosol coolant;
- an air purification system was introduced with a dry type filter and automatic dust extraction from the filter using an ejector, which operated using the energy of exhaust gases;
- colloidal graphite coating of piston skirts;
- removable cermet valve guides;
- molybdenum coating of the lower piston ring;
- active-reactive exhaust noise suppressor.
The note:
“To work as part of a road train, the KamAZ-5320 was equipped with a 210 hp engine, and for single vehicles - with a 180 hp engine.”
The power unit used a double-disc dry clutch. To facilitate the use of the pedal, the hydraulic drive of the clutch control mechanism had a pneumatic booster.
Paired with the engine was a manual 5-speed gearbox, which had synchronizers in second, third, fourth and fifth gears. The gearbox was controlled remotely by a mechanical drive, for which there was a gear shift lever in the cab.
Most of the KamAZ-5320 trucks received a divider, which was an additional two-stage gearbox and was installed after the clutch in front of the main gearbox. One gear of the divider is made direct (that is, the gear ratio is 1), and the second gear is made overdrive (the gear ratio is 0.815). Thus, the divider allows you to double the number of gears and bring them to ten. In the divider, the gears are switched using a pneumatic drive, for which a flag is located on the gearbox lever.
The open type cardan transmission consists of two tubular shafts. Cardan joints are on needle bearings with a constant supply of lubricant. The main gear of the drive axles is made double: a pair of bevel gears with special teeth and a pair of cylindrical helical gears. A symmetrical center differential is installed in the middle axle, distributing torque between the axles. If necessary, the driver could lock the differential from the cab.
Technical characteristics of KamAZ-5320:
- wheel formula – 6×4;
- curb weight – 7184 kg;
- load capacity – 8000 kg;
- towed trailer load capacity – 8000 kg;
- load capacity of the road train – 16000 kg;
- maximum speed of the road train – 85 km/h;
- braking distance of a road train with a full load from a speed of 40 km/h – 21 m;
- control fuel consumption of the road train – 85 l/100 km;
- fuel reserve – 170 l.
Steering
The steering is a screw and nut type on circulating balls with a hydraulic booster, which is combined with the steering mechanism.
Cabin
The three-seater cabover cab of the KamAZ-5320 was attached to the frame and was located above the engine, which provided better visibility for the driver and increased the area of the cargo platform. This arrangement shortened the wheelbase and improved the maneuverability of the truck. To provide access to the engine, the cabin was tilted forward using a torsion mechanism.
Inside the cabin there are three seats with adjustments in the longitudinal direction, height and angle of the backrest and with folding armrests. The driver's seat is equipped with an adjustable torsion bar suspension and a hydraulic shock absorber.
There are two round lamps and a hatch for ventilation on the ceiling.
At the workplace of the KamAZ-5320 vehicle, a steering column with a steering wheel and a combination switch was located in front of the driver. The combination switch was responsible for:
- turning on high and low beam headlights, side lights and instrument panel lighting;
- direction indicators;
- sound signal.
Behind the steering column there was an instrument panel on which indicator lamps, a speedometer, a tachometer, etc. were placed.
To heat the KamAZ-5320 cabin, it was carried out from the engine cooling system using a water radiator with a tap, two fans with electric motors, hot air distributors with dampers and controls.
Loading platform
Behind the cabin, a metal platform with three folding sides was installed on the frame. The platform was equipped with removable arches and an awning to protect the cargo from bad weather.
The base of the KamAZ-5320 truck platform consists of a frame, which is formed by transverse beams, reinforcements, side, rear and front trim and eight wooden floor panels connected by metal strips. The side and rear sides were folding, and the front side was rigidly attached to the base of the platform. The tailgate has steps and chains that hold it in a horizontal, open position.
The sides are locked with corner and side locks. The sides and base frame of the platform have sockets for installing six awning frame posts, which are connected to each other by arches and struts. In the lower part of the awning there are holes for attaching it with a cable to the sealing ears.
A tool box is installed in the front part of the platform on the left side, and the entrenching tool is secured under the platform with special clamps.
Overall dimensions of KamAZ-5320:
- length – 7395 mm;
- width – 2500 mm;
- height – 2830 mm;
- rear bogie base – 1320 mm;
- front wheel track – 2010 mm;
- rear wheel track – 1850 mm;
- ground clearance - 385 mm;
- loading height – 1370 mm.