| K-700 "Kirovets" | |
| Project, g | 1961 |
| Issued, gg. | July 13, 1962 - February 1, 2002 |
| Instances | 401,300 (as of 1995[1]) |
| Purpose | universal |
| Propulsion type | wheeled, all-terrain |
| Traction class, tf | 5/(5) |
| Gross weight, t | 12 |
| Location | |
| Cabin: | average |
| Engine: | front |
| Main Dimensions | |
| Length, mm | 7235 |
| Width, mm | 2530 |
| Height, mm | 3225 |
| Road (agrotechnical) clearance, mm | 440 |
| Engine | |
| Designation according to GOST | 8ChN13/14 |
| Engine make | YaMZ-238NB |
| Transmission | |
| Transmission type | mechanical/hydromechanical |
| Suspension and handling | |
| Suspension type | spring of the front axle, balancer of the rear axle. Some tractors (designed to work with bulldozers and loaders) have a rigid suspension. |
| Rotation control method | turning the semi-frames |
| Brakes | pneumatic wheeled (on early models - pneumohydraulic) |
| Equipment | |
| Hydraulic equipment | a separate separate-module system for controlling mounted and trailed machines; separate system for steering control; separate system for gearbox control |
| Pneumatic equipment | for driving brakes: compressor, buffer tank, pneumatic distributor, wheel brake cylinders |
| Electrical equipment | on-board network with voltage 12V; to start the engine and oil pump switches to 24V |
| K-700 "Kirovets" on Wikimedia Commons | |
K-700 "Kirovets"
is a Soviet general purpose wheeled tractor with all-terrain capability, traction class 5. Designed to be used in conjunction with mounted, semi-mounted and trailed wide-grab agricultural machines (plowing and deep loosening of the soil, cultivation, discing, harrowing, stubble peeling, sowing , snow retention), transport, road construction, reclamation, earthmoving and other works. Chief designer - Joseph Kotin.
Story
In 1961, for the technical re-equipment of agriculture, Soviet designers, on instructions from the government, developed a project for the first Soviet wheeled tractor of traction class 5. With an engine power of 220 hp. with., making it possible to use wide-cut implements, the K-700 increased the productivity of agricultural work by 2.5-3 times compared to other tractors.
Like many other types of equipment in the USSR during the Cold War, the K-700 was developed as a dual-use product: in wartime it was supposed to be used as an artillery tractor[2].
The production of the new machine, named “Kirovets”, was organized at the Kirov plant in Leningrad, the oldest tractor manufacturing enterprise in the USSR.
The first tractor left the assembly shop and entered the fields of the country on July 13, 1962. Mass production of the K-700 began in 1969.
Tractor K-700 on a field in the GDR, 1986
In 1975, the Kirov Plant began serial production of the Kirovets K-700A tractors with an 8-cylinder YaMZ-238ND3 engine (235 hp) and the Kirovets K-701 tractors with a 12-cylinder YaMZ-240B engine (300 hp). With.). The K-700A and K-701 tractors were unified and differed only in the engine, but both were very different from the first K-700, it was already a different tractor. Fundamental differences (not to mention the design) - there are no springs on the K-700A (K-701) (there are on the K-700). Instead of the rear fuel tank (on the K-700), the K-700A (K-701) tractor received two side fuel tanks (left, right) that merge into a single unit with the front wings of the tractor. The K-700A (K-701) has different wheels (not unified with the wheels of the K-700 tractor). This tractor was in demand not only in agriculture, it began to be used in other sectors of the national economy of the USSR. The Kirovets K-703 tractor with a reversible control post was developed. On its basis, the LT-163 timber stacker (after the LT-195 modernization), the ML-56 timber skidding machine, the LB-30 gradedozer, the PF-1 front loader, the DM-15 universal road machine and other machines were created. Various equipment was also developed for installation on the rear semi-frame of the Kirovets K-700A and K-701 tractors: loading P-4, P-4/85, hundred-throwing and others. To perform reclamation and other work, a trencher was developed on the basis of the Kirovets tractor. Seeing the great demand for the Kirovets tractor in other sectors of the national economy, the Kirov Plant began producing various equipment based on the Kirovets tractor in 1990. It was road construction and special equipment. For the needs of road workers and workers in other industries, the Kirov Plant began to produce the K-702MA-PK6 front loader, the K-702MBA-BKU universal bulldozer, the K-702MVA-UDM universal road machine, the VK vibratory roller, the SFR snow blower, mobile welding units for 4 and 8 welding posts and other equipment.

Monument to a tractor in one of the Ukrainian cities
On February 1, 2002, the St. Petersburg Tractor Plant stopped producing the Kirovets K-700A and K-701 tractors.[3] Instead, the Kirovets K-744 tractors began to be produced, which were much more expensive than the Kirovets K-700A and K-701 tractors. Plant managers explained the removal of the Kirovets K-700A and K-701 tractors by saying that these tractors were obsolete and their cabins did not meet safety standards. In this regard, there was a shortage of inexpensive tractors of the Kirovets type.
Many years of experience in operating the machine in various conditions and climatic zones have shown high reliability, simplicity and ease of maintenance, maintainability and long service life.[4]
Unfortunately, there were also disadvantages. In conditions of extremely significant unevenness of the road surface, it was possible for the car to overturn. The protruding engine worsened cross-country ability in extreme conditions. Agronomists demanded machines with less pressure on the ground. These shortcomings were never eliminated in the K-744.
Due to the demand, tractors of the K-700 series (both original models of the Kirov plant and various modifications), as well as tractors, bulldozers, loaders and special machines based on them continue to be produced by various engineering enterprises in Russia.
CJSC Petersburg Tractor Plant currently produces only special-purpose equipment based on the K-700. Agricultural tractors of the K-700 series under the Kirovets brand are no longer officially produced, and those on the market are usually restored from old ones and have very dubious origins.
As of 2020, Petersburg Tractor Plant JSC produces two models of agricultural tractors - K-744R and K-703M - in various configurations.[5]
Modifications of K-701
- K-701 PF-1 is a front-end loader that can easily cope with absolutely any unloading and loading work.
- K-701 PF-1 is a timber stacker. This modification was based on the previous one. The only difference is the jaw grip, which was installed instead of the bucket. This technique was designed for loading logs or pipes.
- The K-701M tractor is a self-propelled vibratory roller. Such equipment was intended to be used in road, hydraulic engineering and airfield construction for compacting cohesive and non-cohesive soils.
For quite a long time, the K 701 tractor had absolutely no analogues. But soon the UDM-5K-1 appeared, which had similarities in dimensions, tasks and load capacity.
Modifications

K-703M-AS8-200
- K-700
- basic model. - K-700A
- the next model (unified with K-701, YaMZ-238ND3 engine with turbocharging). - K-701
- the next model (unified with K-700A, YaMZ-240BM2 engine).[6] - K-701M
- modification with a YaMZ 8423.10 engine with a power of 335 hp. With. In 1979, driver-inventors from Chukotka built four six-wheeled vehicles based on the K-700, which 10 years later served as prototypes for an experimental factory modification[7]. - K-702
is an industrial modification for use as a base machine for loaders, bulldozers, rollers, scrapers: the linkage system has been changed, only a hydromechanical transmission is used, and the suspension is rigid. - K-703
- industrial modification. The tractor has a reversible control post, allowing the operator to work in a normal position both when the tractor is moving forward and when the tractor is moving backward. - K-703MT
is a three-axle articulated dump truck with a lifting capacity of 18 tons.[8]
Technical characteristics of K-701, weight
The K-701 model was intended for various types of work in conjunction with wide-cut equipment. The tractor consists of two semi-frames that rotate relative to each other vertically and horizontally thanks to hinges. The front and rear axles are driven and rigidly connected to the frame. The rear axle can be disabled. The transmission is also represented by a semi-rigid coupling with rubber elements, a manual gearbox, and a cardan drive with needle bearings (open type).
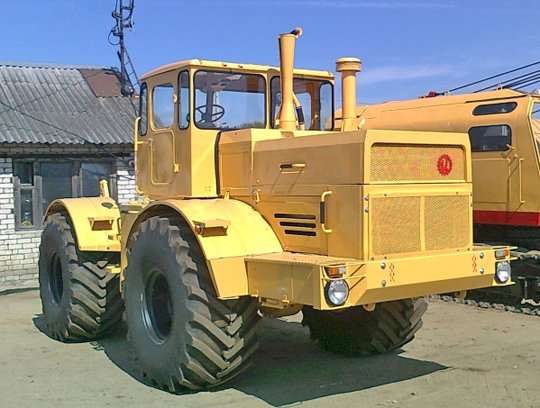

Photo source: kowsh.ru Photo K-701
The drive axles consist of a main gear (two bevel gears with circular teeth), a self-locking freewheel differential and a final drive (single-row planetary gearbox).
Control is carried out using two hydraulic cylinders, a worm gear and a spool-type hydraulic distributor. Discless wheels are equipped with working drum brakes with pneumatic drive. A parking shoe-disc brake is installed on the front axle.
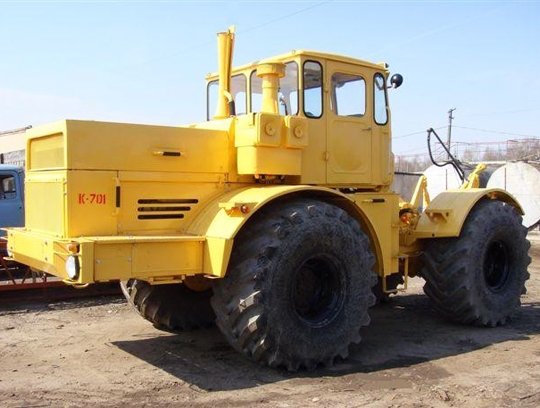

Photo source: kostroma.tiu.ru The structural weight of the K-701 with main equipment is 12,400 kg
Transmission

Tractor gearbox K-700
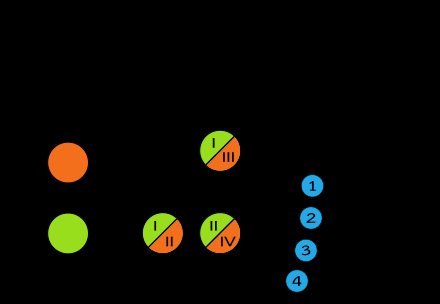
The K-700 tractor does not have a clutch. Instead, there is a drain pedal (pressure drop in the gearbox hydraulic system). The gearbox is mechanical, with constant mesh gears, 16-speed (four-mode), with hydraulically controlled four clutches and mechanically controlled gear clutches. All gears are spur gears.[9] Number of gears (hydraulic) 4 (+2 neutral), 4 modes (mechanical), high-low switching. As a result, the number of speeds is 16 (from 1.1 to 4.4) and, accordingly, 8 rear. The box is designed to change gears without loss of power (due to friction clutches). Modes are switched by moving gears as in any manual transmission. Speeds are switched by switching the spool (by redirecting the hydraulic oil flow). The 2nd neutral turns off the hydraulic flow. The 1st neutral, in addition to turning off the hydraulic flow, mechanically slows down the drive shaft (shaft with clutches) in the gearbox like a hand brake. Therefore, you can turn on the 1st neutral only after stopping.
Specifications
- Overall dimensions: Length, mm 8400
- Width, mm 2530
- Speeds: when moving forward 2.9-44.8 kilometers per hour
- when moving backwards 5.1-24.3 kilometers per hour
- Minimum turning radius, mm 7200
- Track width, mm 2115
- Engine power YaMZ-240B 300 hp. s., at a rotation speed of 1900 min-1. Maximum torque 1240 Nm.
- Engine power YaMZ-238NB 280 hp. s., at a rotation speed of 1700 min-1. Maximum torque 950 Nm.
- Weight of K-700 A 12.8 tons.[4]
- K-701 weight 13.5 tons.[10]
Technical characteristics of Kirovets K 701
| Engine power, kW (hp) | 221 (300) |
| Specific fuel consumption, g/kWh | 258 |
| Travel speed, km/h | 2,6 – 33,8 |
| Number of gears: | |
| - forward | 16 |
| - back | 8 |
| Load capacity of three-point hitch, kN | 56 |
| Travel of the suspension axis of the mounted device, mm | 1175 |
| Overall dimensions, mm | |
| - length | 6820 |
| - width | 2850 |
| - height | 3685 |
| weight, tons | 13,4 |
The technical characteristics of the K701 tractor allow us to call it a “hero”; it is precisely thanks to its power that it is still in demand in industrial and popular sectors.
Notes
- Domestic agricultural tractors. History of development over 100 years.//A team of authors from NATI, the Moscow region branch of NATI and the Museum of Tractor Equipment together with specialists from tractor factories. - M.: 1996
- Followers of Kegress. Around the World No. 3 (2810) | March 2008
- Key milestones in the development of tractor engineering at the Kirov Plant Archived copy dated January 24, 2012 on the Wayback Machine // Official website of Petersburg Tractor Plant CJSC.
- ↑ 12
Tractor Kirovets K-700A // K-700.ru - Description of products on the website of the St. Petersburg Tractor Plant Archived copy dated May 8, 2020 on the Wayback Machine
- Mosfinance LLC.
K-701 Slavich. Agricultural wheeled tractor. www.rus-parts.ru/. — Description and technical characteristics of the model. Retrieved December 2, 2008. Archived March 15, 2012. - Pogonichev vs. Kremko 24. “Behind the Wheel” (No. 3, 1990). Retrieved February 4, 2020.
- K-703MT 6. “ZR” (No. 4, April 1994). Retrieved May 23, 2020.
- Tractors “Kirovets” L. I. Bezverkhny, A. I. Ostrovsky Moscow Agropromizdat 1986
- K-701
- Tractor K-704-4R “Stanislav”, “ProfTechKomplekt”.
- K-704-4R “STANISLAV” UNIVERSAL AGRICULTURAL TRACTOR, “AGROCENTER”.
- Agricultural tractor K-704-4R “STANISLAV” Archival copy dated July 26, 2020 on the Wayback Machine, “KaravanAgroTrade Naberezhnye Chelny”.
- FIRST tractor in the Tyumen region K-704 “STANISLAV”, “Gagarinskremtekhpred”.











