Technical examination of the crane allows us to determine its condition for compliance with the rules of GosgorTekhnadzor and the documentation issued during registration. During the inspection, the date and results of the inspection are recorded in the crane passport. Technical examination can be either full or partial. A full technical inspection of cranes is carried out at least once every three years. Partial - at least once a year.
carries out major repairs and maintenance of truck cranes, aerial platforms, hydraulic manipulators with Full and Partial technical inspection, and also installs and repairs safety devices.
A full survey is an inspection that includes static and dynamic testing. An extraordinary full technical examination is carried out after installation caused by the relocation of the crane to a new location, as well as after reconstruction of the crane, major repairs of the lifting mechanism, replacement of the hook suspension hook, repair of metal structures with replacement of design elements or components.
Partial inspection - inspection, without static and dynamic testing. After replacing worn-out cargo, boom or other ropes, as well as after re-roping the ropes, the Rules require a partial inspection to be carried out to check the correctness of the reeving and the reliability of fastening the ends of the rope, as well as the wrapping of the ropes with a working (nominal) load.
The purpose of the inspection is to check the condition of the crane and its mechanisms. During the inspection, the operation of the electrical equipment and mechanisms of the crane, safety devices, brakes and control devices, lighting, alarms, metal structures of the crane, the hook and its suspension parts, ropes and their fastenings, blocks, axles and their fastening parts, as well as boom suspension elements are checked; control whether the crane is installed correctly, what condition the crane tracks are in, whether they are grounded, whether the mass of ballast and counterweight corresponds to the values specified in the crane passport.
The purpose of the static test is to test the crane for strength and load stability. Static testing is carried out under a load exceeding the crane's lifting capacity by 25%. To do this, the load raised to a height of 200 mm is held for 10 minutes. After lowering the load, inspect the lifting mechanism and check the metal structures of the crane for the absence of residual deformations. If the crane has several load characteristics, the test is carried out at flights corresponding to the most stressed state of the mechanisms, metal structures, ropes and the least stability of the crane,
The purpose of the dynamic test is to check the operation of the crane mechanisms and their brakes. Dynamic tests are carried out with a load exceeding the crane’s lifting capacity by 10%. It is allowed to carry out dynamic tests with a working (nominal) load. During dynamic testing, the load is repeatedly lifted and lowered, as well as the operation of all other crane mechanisms is checked when moving this load.
The results of the technical examination are entered into the crane passport indicating the date of the next examination. When inspecting a newly installed crane, it is written in the passport that the crane was installed in accordance with the Rules of GosgorTekhnadzor, operational documentation and has passed the tests.
Takes upon itself the maintenance and repair of cranes of any modifications. PTO overhead crane. WHAT and PTO of beam cranes. Inspection of gantry cranes, Liebherr and Potain cranes. Checking all construction equipment in your fleet.
Classification
To begin with, it should be noted that the above classification cannot fully reflect all existing types of cranes, since many are located on the borders of the presented points, or combine them.[23]
Design
Load-lifting cranes can be divided into the following main types by design:
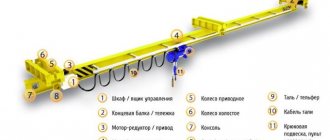
Jib-type cranes The load-handling member is suspended from a boom or a trolley moving along the boom. These include tower, portal, semi-portal, jib cranes, etc. Bridge type cranes The supporting structure has the form of a bridge with a trolley or electric hoist moving along it. These include overhead, gantry, semi-gantry, cantilever cranes, bridge cranes, stacker cranes, etc. Cable-type cranes A load-handling member is suspended from a cargo trolley moving along load-bearing ropes fixed in supports.
Tower crane Liebherr-710 HC-L 32/64 Litronic
Possibility of moving
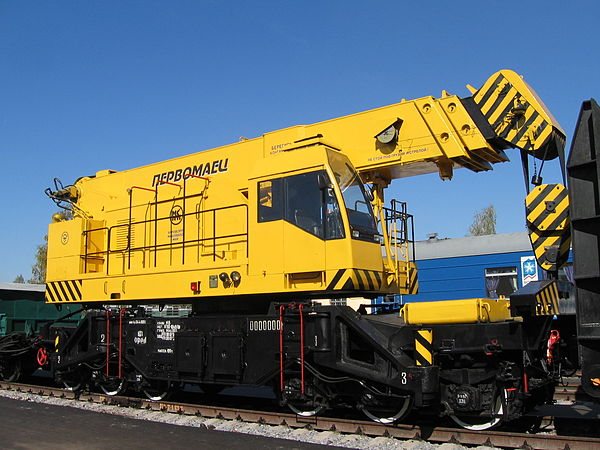

Railway crane KZh-971 The stationary crane is fixedly fixed to the base and cannot be moved. The radial crane has the ability to move along a circular path relative to a stationary support. Radial cranes are used in round or sector-shaped warehouses. The adjustable crane is fixed to the base and can be moved using lifting machines or manually. Self-lifting crane is used in construction. Installed on the structures of a building under construction. As the structure is erected, the crane rises upward using special mechanisms. The crane is a quick-installed tower crane, installed on site using its own mechanisms, without steeplejack operations and with an operational installation time of no more than 30 minutes. The mobile crane has the ability to move. Types of mobile cranes: Self-propelled crane (has the ability to move during operation and transport cargo due to the supply of electricity using the following systems: trolley busbar, contact rail, overhead cable systems, cable drum with a spring or motor drive, contactless power transmission system); Trailed crane (moved by tug using a trailer).
type of drive
Manual drives are used when moving loads over short distances and at low work rates. Electric drive In electric drive cranes, mainly AC electric motors are used; if speed control is necessary, frequency converters or DC electric motors are used. For work in fire and explosion hazardous areas, electric motors in fireproof and explosion-proof designs are used. The hydraulic drive is compact, allows for stepless adjustment of crane speeds, but has low efficiency. Pneumatic drives are mainly used when working in fire and explosive environments. Equipped with an internal combustion engine, they are used in cranes that operate independently of the electrical network: mobile automobile, railway, crawler, floating.
Rotation degree
According to the degree of rotation of the crane, there are two types:
The rotary valve has the ability to rotate relative to the support. Rotary valves can be full-rotary (angle of rotation more than 360°) and not full-rotary (angle of rotation less than 360°). A fixed crane cannot rotate relative to the support.
Support type
According to the type of support, cranes are divided into: support, suspended, pneumatic wheels, automobile, rail, railway, tractor, crawler cranes, wheeled cranes, cranes on a special chassis.
Type of load-handling device
Portal crane with grab Hook cranes The load-handling element of the crane is the hook.
This is the simplest and oldest device, which is widely used in almost all types of taps. Grab cranes, the load-handling element of the crane is a grab. Magnetic cranes, the load-handling element of the crane is an electromagnet. Clamp-on cranes, the load-handling element of the crane is tongs. Container cranes, the load-handling element of the crane is the spreader. There are also pin cranes, stacker cranes, foundry cranes, stripper cranes, landing cranes, well cranes, magnetic grab cranes, forging cranes, etc. The load-handling member is selected depending on the characteristics of the load.
Scope of work during technical inspection of cranes
When carrying out a technical inspection of cranes, it is necessary to inspect and check the operation of its mechanisms, brakes, hydraulic and electrical equipment, instruments and safety devices. Checking the serviceability of the load limiter of a jib-type crane should be carried out taking into account its load characteristics.
In addition, during the technical inspection of the crane the following must be checked:
a) the condition of the metal structures of the crane and its welded (riveted) connections (no cracks, deformations, thinning of walls due to corrosion, weakening of riveted connections, etc.), as well as the cabin, stairs, platforms and fences;
b) the condition of the hook and blocks. For cranes transporting molten metal and liquid slag, for ladle lifting and tilting mechanisms, inspection of forged and stamped hooks and parts of their suspension, as well as suspension parts of plate hooks, must be carried out by the factory laboratory according to instructions using non-destructive testing methods at least once every 12 months . The laboratory report must be stored together with the crane passport.
c) the actual distance between the hook suspension and the stop when the limit switch is activated and the lifting mechanism stops (must be at least 200 mm for cranes);
d) the state of insulation of wires and grounding of the electric tap with determination of their resistance;
e) compliance of the mass of the counterweight and ballast of the jib crane with the values specified in the passport;
f) the condition of the rail track, its compliance with the substation operating manual, the project, as well as the requirements of these FNP;
g) the condition of the ropes and their fastenings;
h) state of lighting and alarm.
Static tests of the crane are carried out with a load 25% greater than its rated load capacity.
Static tests of an overhead crane are carried out as follows. The crane is installed above the supports of the crane track, and its trolley (trolleys) is installed in a position corresponding to the greatest deflection of the bridge. The test load is lifted by crane to a height of 100 - 200 mm and maintained in this position for 10 minutes.
After 10 min. the load is lowered, after which the absence of residual deformation of the crane bridge is checked. If there is residual deformation resulting from testing the crane with a load, the crane should not be allowed to operate until a specialized organization has clarified the causes of the deformation and determined the possibility of further operation of the crane. Static testing of gantry crane and overhead material handler is carried out in the same way as overhead crane testing; in this case, for a crane with consoles, each console is tested separately.
Static tests of a jib-type crane having one or more load characteristics are carried out in a position corresponding to the crane's maximum load capacity. During static tests of jib-type cranes, the boom is installed relative to the running support in a position that corresponds to the lowest design stability of the crane, and the load is raised to a height of 100 - 200 mm. The crane is considered to have passed static tests if within 10 minutes. the lifted load will not fall to the ground, and cracks, residual deformations and other damage to metal structures and mechanisms will not be detected.
Dynamic tests of the crane are carried out with a load whose mass is 10% greater than its rated load capacity, and are aimed at checking the operation of its mechanisms and brakes.
During dynamic testing of cranes (except for cable-type cranes), the load is lifted and lowered multiple times (at least three times), as well as the operation of all other mechanisms is checked when combining working movements provided for in the crane operating manual. For a crane equipped with two or more lifting mechanisms, each mechanism must be tested.
To conduct static and dynamic tests, the crane owner must ensure the availability of a set of test (control) weights indicating their actual weight. Technical examination of cranes (cranes) must be carried out by a specialist responsible for carrying out production control during the operation of the substation with the participation of a specialist responsible for the safe performance of work using lifting structures intended for moving goods.